
Tuesday, February 18, 2025
Kevin Anderson
As organizations increasingly adopt multiple Software as a Service (SaaS) tools—spanning CRM, project management, HR, finance, and more—the complexity of managing all these subscriptions grows in tandem. The result is often “SaaS sprawl,” where various teams purchase and maintain separate apps, each with its own login credentials, renewal schedules, compliance requirements, and usage patterns. Enter SaaS management platforms: solutions that promise to centralize oversight, reduce wasteful spend, and enhance security.
However, do these management platforms deliver on their pledge to tame the chaos, or do they risk turning into another monthly bill that ironically adds to the confusion?
In line with the Escape the SaaS Trap philosophy—which warns about hidden costs and vendor lock‑in—this article unpacks both the value and potential downsides of these management solutions. We’ll also identify critical features that make a genuine difference in multi‑SaaS environments, as well as outline the “Smart SaaS oversight” approach that ensures real ROI.
Navigate through the article using the links below:

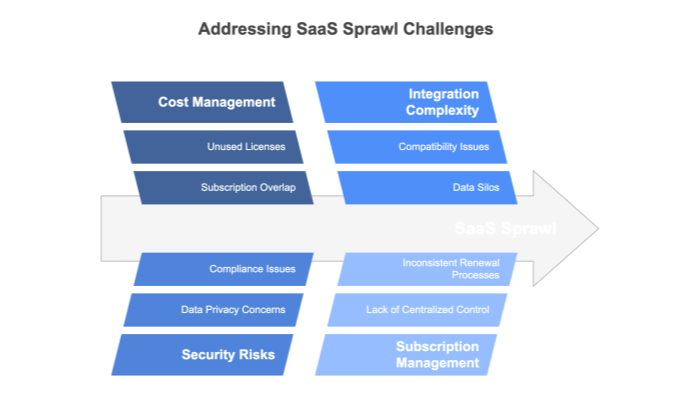
In today’s dynamic business environment, the proliferation of specialized SaaS tools has led to a phenomenon known as SaaS sprawl. As each department seeks the best-in-class software to address its unique needs, organizations can end up with a sprawling collection of subscriptions that lack coordination.
This uncontrolled growth often results in overlapping functionalities, inconsistent renewal dates, and significant security blind spots. The challenges include managing user access when employees leave, tracking renewal dates, and reconciling data spread across multiple platforms.
In this section, we examine the factors driving SaaS sprawl and discuss both its benefits and drawbacks.
Key Benefits:
- Quick Adoption: Departments quickly implement specialized tools.
- Targeted Functionality: Each tool is designed for a specific purpose.
- Minimal IT Overhead: SaaS solutions reduce the burden on internal IT teams.
However, drawbacks include:
- Overlapping Tools: Multiple apps performing similar functions.
- Inconsistent Renewals: Renewal dates vary across subscriptions.
- Security Blind Spots: Lack of centralized oversight can lead to vulnerabilities.
Key Challenges:
- Poor Access Management: Ex‐employees might retain access to several platforms.
- Overlooked Renewals: Auto‑renewals can result in unexpected high costs.
- Siloed Data: Disparate systems complicate compliance with privacy regulations.
Additional Insight:
Without a centralized system, departments work in isolation, leading to inefficient use of resources and increased operational costs. The lack of integration between various tools also creates data fragmentation, which can hamper decision‑making and risk management.

SaaS management platforms (SMPs) are designed to provide organizations with a unified view of their entire SaaS ecosystem. They centralize subscription tracking, access management, usage monitoring, and compliance oversight into one cohesive tool. By doing so, SMPs aim to reduce waste, enhance security, and optimize overall software spend. In this section, we discuss the core concept behind these platforms and outline their potential benefits for IT, finance, and department heads.
Main Functions:
- Tracking Subscriptions: Monitor which apps are in use, the number of seats, and renewal dates.
- Coordinating Access Management: Automate provisioning and deprovisioning of users.
- Usage Monitoring: Keep an eye on metrics such as daily usage and cost per seat.
- Policy Enforcement: Ensure compliance with security standards and industry regulations.
Key Advantages:
- Centralized Visibility: A single dashboard consolidates all subscription data.
- Cost Optimization: Identify redundant or underutilized licenses to save money.
- Streamlined Onboarding/Offboarding: Simplify user management across multiple apps.
- Enhanced Security: Enforce consistent access policies and compliance standards.

A robust SaaS management platform should offer a range of functionalities that address the key challenges of managing a multi‑SaaS environment. This section outlines the essential features that ensure an SMP can deliver true value by streamlining operations, optimizing costs, and enhancing security. Each functionality plays a critical role in transforming disparate SaaS applications into a cohesive, manageable ecosystem.
Key Features:
- Automated Deprovisioning: Prevents ex‑employees from accessing critical apps.
- Granular Role Assignment: Allows detailed control over user privileges.
- SSO Integration: Reduces password sprawl and simplifies login processes.
Key Features:
- Itemized Billing: Consolidates costs from various subscriptions into one dashboard.
- Department-Level Tracking: Tags subscriptions by cost center for precise budgeting.
- Alert System: Notifies stakeholders when spending exceeds set thresholds.
Key Features:
- Data Sharing Risk Scans: Identifies potential security vulnerabilities.
- Certification Monitoring: Tracks compliance renewals for critical apps.
- Access Rule Enforcement: Alerts if third-party integrations bypass security protocols.
Key Features:
- Automatic Detection: Identifies unauthorized or non‑procured SaaS tools.
- Spend Analysis: Reveals hidden expenses and overlapping functionalities.
- Security Gap Identification: Highlights potential vulnerabilities in unapproved apps.
Key Features:
- SaaS Portfolio Overviews: Summarizes all active subscriptions and their costs.
- License Utilization Reports: Indicates which licenses are active versus idle.
- Vendor Performance Metrics: Monitors downtime and user satisfaction to evaluate providers.

While SaaS management platforms promise centralized oversight and cost savings, they can sometimes add another layer of complexity—and cost—to an already sprawling environment. This section discusses whether adopting an SMP is a genuine solution or simply another subscription that contributes to SaaS bloat. We examine potential pitfalls and highlight considerations that businesses should take into account before implementing an SMP.
Common Risks:
- Overpriced Solutions: High fees that may not be justifiable for smaller organizations.
- Underperforming Tools: Lack of robust integrations and limited dashboard capabilities.
- Another Lock-In Risk: SMPs that tie you to proprietary systems.
Key Considerations:
- Redundancy: Avoid duplicating functions already managed by your IAM or financial tools.
- Cost Efficiency: Evaluate if an internal solution might be simpler and cheaper.
- Integration: Determine whether the SMP will integrate seamlessly with your existing processes.
Insight:
- Counterproductive Growth: Adding an SMP can sometimes feed into the cycle of acquiring more SaaS tools.
- Risk of Shelfware: An SMP that is rarely used ends up being another wasted subscription.
- Strategic Alignment: It’s essential to ensure the SMP aligns with your overall business processes and isn’t just an extra tool.

For a SaaS management platform to truly add value, it must deliver on its promise of smart oversight. This section details the core features that any effective SMP should offer to ensure transparency, cost control, and robust security compliance. By focusing on these features, businesses can achieve centralized management without compromising on flexibility or data ownership.
Features:
- One Pane of Glass: Integrates data from all SaaS tools for a comprehensive overview.
- Real-Time Metrics: Displays live usage, cost, and renewal information.
- Consolidated Reporting: Offers detailed, up-to-date reports for informed decision-making.
Features:
- HR Integration: Automatically provisions new hires across all relevant apps.
- Immediate Deprovisioning: Cuts off access for departing employees to enhance security.
- Simplified User Management: Streamlines the entire lifecycle of user accounts.
Features:
- Contract Storage: Maintains a digital repository of all vendor contracts.
- Renewal Alerts: Sends timely notifications to renegotiate or cancel auto‑renewals.
- Cost Optimization: Identifies opportunities to reduce subscription fees.
Features:
- Quota Monitoring: Tracks usage against plan limits to avoid overage fees.
- Data Correlation: Links usage metrics with cost data for actionable insights.
- Alert System: Notifies stakeholders when usage nears thresholds.
Features:
- Single Sign‑On (SSO): Provides a unified access portal for all SaaS apps.
- Compliance Audits: Regularly checks for adherence to industry security standards.
- Anomaly Detection: Flags unusual access patterns or usage spikes.

One of the most critical questions for any organization considering an SMP is whether it delivers a positive return on investment. In this section, we explore the various ways an SMP can lead to cost savings, productivity gains, and risk reduction. By measuring these benefits against the platform’s cost, businesses can determine if the solution truly pays for itself. We discuss key metrics and strategies to ensure that the investment in an SMP is justified and contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Strategies:
- License Optimization: Identify and eliminate unused or underutilized licenses.
- Vendor Consolidation: Unify overlapping tools to reduce redundant spending.
- Timely Renewals: Negotiate better terms before auto‑renewals occur.
Benefits:
- Centralized Onboarding: Streamlines employee onboarding processes.
- Efficient Management: Reduces manual tasks related to license tracking and renewals.
- Time Savings: Frees up IT and HR teams for more strategic work.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Consistent enforcement of access policies lowers breach risks.
- Compliance Assurance: Mitigates the risk of fines from regulatory non‑compliance.
- Operational Continuity: Avoids costly disruptions from unmanaged subscriptions.
Checklist:
- Transparency: Are all costs and metrics clearly visible?
- Agency: Can the SMP be adapted to your specific workflows?
- Data Ownership: Is it easy to export data if needed?
- Security: Does the platform adhere to strong security standards?
- Scalability: Will it grow cost‑effectively with your SaaS portfolio?

To avoid falling into another subscription trap, it is essential to recognize the red flags of an ineffective SMP. This section highlights warning signs that indicate an SMP may not be delivering its promised benefits. By paying close attention to these signals, organizations can make more informed decisions and steer clear of solutions that might exacerbate SaaS sprawl rather than mitigate it.

Effective oversight of your SaaS environment requires a systematic approach. This section outlines practical steps to implement a "Smart SaaS oversight" strategy that aligns with your organization’s goals. From conducting a comprehensive audit to negotiating reasonable pricing and piloting integrations, these actionable steps help ensure that your SMP not only consolidates subscriptions but also delivers measurable value in terms of cost savings, security, and efficiency.
Steps:
- Inventory Tools: List all SaaS applications currently in use.
- Assess Pain Points: Identify which processes are most cumbersome.
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you aim to achieve—cost reduction, enhanced security, or improved compliance.
Guidelines:
- Departmental Pilot: Start with one department to test the SMP’s capabilities.
- Monitor Onboarding: Evaluate if user provisioning is genuinely simplified.
- Assess Data Accuracy: Check if the cost dashboards and usage metrics are reliable.
Tips:
- Scalable Pricing: Ensure the pricing model grows reasonably with your usage.
- Avoid Multi-Year Lock-In: Opt for flexible contract terms.
- Clarify Cost Structure: Understand fees per admin, per app, or based on total spend.
Key Principles:
- Transparency: All costs and usage data should be openly displayed.
- Agency: The platform must be adaptable to your workflow.
- Ownership: Secure data export options are essential.
- Security: Ensure robust security measures are in place.

A SaaS management platform can be a powerful tool to rein in the chaos of a sprawling multi‑SaaS environment. It offers centralized oversight, cost optimization, streamlined access management, and enhanced security. However, if not carefully chosen and implemented, it can simply add another layer of subscription fees and complexity. This conclusion emphasizes the importance of adopting a “Smart SaaS oversight” approach—one that prioritizes transparency, data ownership, and security—while ensuring that the chosen platform delivers tangible ROI. Ultimately, the decision to invest in an SMP should be based on a thorough evaluation of your organization’s needs, the platform’s ability to integrate with existing systems, and its potential to reduce costs and risks over time.
Key Takeaways:
- Identify Real Needs: Evaluate if your organization struggles with cost tracking, access management, or compliance.
- Demand Transparency: Insist on clear integration methods, pricing structures, and data policies.
- Pilot First: Test the SMP with a subset of apps to verify its benefits.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Ensure that the savings and efficiency gains outweigh the subscription fees.
- Adhere to Smart SaaS Principles: Always prioritize solutions that maintain data ownership, security, and flexible usage terms.
Below are some commonly asked questions about SaaS management platforms, along with clear and concise answers to help guide your decision‑making process.
