

Wednesday, March 26, 2025
Kim Jamerson
A common misconception about software‑as‑a‑service (SaaS) data security is that it’s the vendor’s responsibility. In reality, the bulk of data security responsibilities lies with the user.
So whether you're buying your first SaaS application or already have a SaaS ecosystem—organizations use a whopping 112 SaaS apps on average—it’s critical that you, your IT and security teams, and all employees understand the roles each play in protecting sensitive information.
Failure to take SaaS data security seriously puts your business in jeopardy, as data breaches can damage your reputation, cripple business operations, and result in financial and legal penalties.
In this article, we’ll discuss key tools for protecting SaaS data, common security risks, best practices and emerging trends in SaaS data security.

SaaS data security is focused on procedures and practices designed to safeguard sensitive user data stored in SaaS applications. Maintaining data integrity and confidentiality in SaaS requires various tools and approaches, such as encryption, access controls, employee training, and adherence to compliance regulations.

SaaS data security can be complex. A good place to start is by understanding three key topics: data, encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and compliance frameworks.
Data encryption is essential throughout your tech stack. It ensures that data is masked instead of immediately visible in the event of a breach. Various security protocols and tools, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), transport layer security/secure sockets layer (TSL/SSL), and HTTPS, are available to assist with encryption.
But it’s important to keep two data concepts in mind as you determine your approach to encryption:
Remember that ensuring these protocols, encryption keys, etc., are in place often falls on the user’s shoulders, so clarify responsibilities with your SaaS provider.
IAM is a security framework that ensures that the right people have access to the right resources at the right time and, conversely, prevents the wrong people from ever gaining access.
Robust authentication approaches go beyond basic username‑password combos and employ tools like single sign‑on (SSO), multi‑factor authentication (MFA), or biometrics to confirm users are who they say they are.
Strong authorization tools and protocols incorporate role‑based access controls, which establish permissions based on a user’s role (e.g., administrator, editor, viewer), or attribute‑based access controls. Attribute‑based controls grant or limit access using anything from user attributes (e.g., location, department) and resource attributes (e.g., data sensitivity, file type) to environmental attributes, such as time of day or network location.
Good accounting tools go beyond capturing activity history; they monitor access to identify suspicious activity or patterns and alert you to take action.
Beyond the reputational and operational risks associated with SaaS data security, regulatory requirements often come into play, depending on your industry and the type of data you’re housing. For example, healthcare and financial services verticals have stringent rules dictating where, how, and what data can be stored and shared. Additionally, regardless of the type of business you operate, sensitive data, like HR and customer information, can trigger privacy, confidentiality, and security rules.
Work with your legal, IT, and compliance experts to understand which national, regional, and local laws and regulations apply based on where you’re located and conducting business. For example:
In addition to legal requirements, there are security frameworks that have become industry standards for SaaS data security, such as:
Many data security laws and regulations require SOC 2 or ISO 27001 certifications to be compliant.

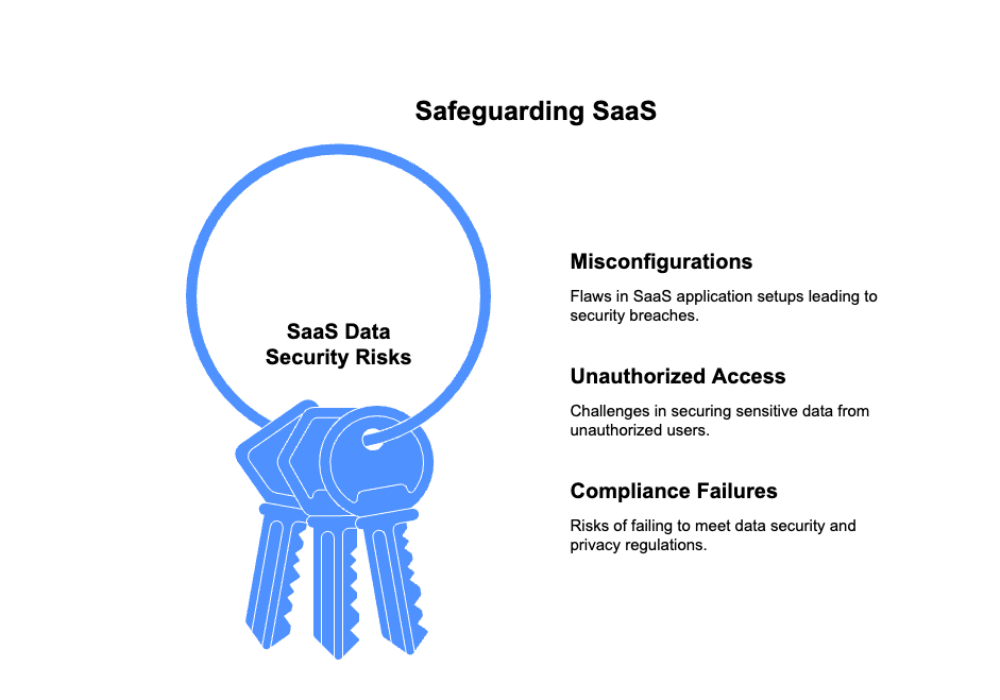
Common risks to SaaS data security include issues stemming from misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and compliance failures. Understanding these risks is essential to taking proactive measures.
A frequent problem with SaaS data security is misconfigurations—flaws in the setup or configuration of SaaS applications that can lead to security breaches, data loss, or other operational problems. According to Cloud Security Alliance research, 43% of organizations surveyed can tie at least one security issue to a SaaS misconfiguration. Unfortunately, nearly half of organizations only check for these misconfigurations monthly or less frequently, and 5% never check for them. Yikes!
According to BetterCloud’s 2024 State of SaaSOps report, three‑quarters of IT professionals surveyed feel their team is responsible for protecting sensitive data within SaaS apps, but 45% say they struggle to secure users’ activities on these platforms.
Strong authentication and authorization protocols are your first defense against unauthorized access to networks, applications, and specific data. However, you must take steps to monitor whether these precautions are effective. Many SaaS solutions include monitoring and tracking tools, but advanced security accounting tools—such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems—are often necessary. SIEM systems continuously analyze security data from various sources across your applications and networks to proactively detect potential threats, vulnerabilities, and suspicious activities in real time.
Failing to comply with data security and privacy regulations can have widespread financial and legal consequences. A few of the largest data breach fines and penalties include:
While SaaS platforms often offer functionality to help meet regulatory standards and requirements, you are ultimately responsible for ensuring your company and employees comply.


The biggest worries that keep IT professionals up at night, according to a BetterCloud survey, include unsanctioned apps that store sensitive data (34%), sensitive files shared publicly (34%), and not knowing where sensitive data exists (31%).
As you work to mitigate SaaS data security risk, here are three best practices to consider.
| SaaS Data Security Best Practices | Related SaaS Security Risks |
|---|---|
| Multi‑Factor Authentication (MFA) | Unauthorized Access |
| Security Audits and Assessments | SaaS Misconfigurations |
| SaaS Data Compliance Tools | Data Security and Privacy Compliance Failures |
MFA adds a critical layer of security to your authentication protocols. When passwords are compromised through phishing or hacking attempts, MFA reduces the risk of account takeover and can prevent access to other sensitive data.
Additionally, companies should set up and enforce policies that require complex passwords and require users to update them frequently. They should also provide regular employee training about the risks of phishing and other social-engineered cyber attacks designed to trick users into sharing confidential information.
With data security, you can’t take a set-it-and-forget-it mindset. It’s important to regularly audit and assess individual application settings and activity logs, as well as to look at how those applications fit into your broader technology portfolio.
Be alert for SaaS misconfigurations, which can range from simple mistakes in user access controls to more complex issues like improperly configured data encryption or API settings.
Conducting manual audits and assessments is time-consuming. More than a third of IT professionals report that meeting quarterly audit requirements takes 10% to 25% of their time. Another 20% say it takes between 25% and 50% of their time to get the job done. (Source: BetterCloud)
Fortunately, SaaS data compliance tools can automate many of these tasks. SIEM systems, as mentioned previously, often include the ability to detect and resolve issues automatically. SaaS management platforms (SMPs) have similar capabilities as well as license usage monitoring, which can assist with cost reduction and capability redundancies.

Like most areas in tech, SaaS data security continues to evolve. Emerging trends are incorporating advanced technologies and innovative practices to further enhance data protection. Organizations are increasingly adopting cutting‑edge solutions to stay ahead of cyber threats and regulatory changes.
These capabilities can enhance real‑time threat detection by analyzing large volumes of data and identifying anomalies in user behavior, network traffic, and system logs. They enable automated response mechanisms that adapt quickly to emerging cyber threats, thereby improving the overall security posture.
This cybersecurity strategy assumes no user or device is inherently trusted and requires continuous verification and strict access controls for every request. Implementing ZTA can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access by ensuring that all interactions are rigorously authenticated and monitored.
Automating data privacy measures helps organizations enforce compliance by automatically applying privacy controls such as data masking, access restrictions, and deletion protocols. This not only streamlines compliance efforts but also ensures consistent application of data protection policies across all SaaS applications.

Establishing a secure SaaS environment requires a holistic strategy that combines technical safeguards, robust policies, and continuous employee training. By working closely with legal, IT, and compliance teams, organizations can develop comprehensive security frameworks that adapt to evolving threats and regulatory requirements. This integrated approach helps protect sensitive information and maintains the integrity of the SaaS ecosystem over time.
For more information about SaaS data compliance tools and best practices, check out these additional SaaS security resources:
Below are some common questions regarding SaaS data security:
There isn’t a single security measure that’s most crucial, but three important components include:
Robust SaaS data security relies on a combination of these measures, which build upon each other to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Failure to establish and follow SaaS data security policies can result in data breaches that can have far-reaching consequences for your business, including reputationally, operationally, financially, and legally.
When managing SaaS security, leveraging the right tools is essential for capturing, validating, and publishing security data effectively. Examples include:
These tools help organizations maintain security visibility, enforce compliance, and mitigate risks across SaaS ecosystems.