

Friday, March 7, 2025
Kevin Anderson
Software as a Service (SaaS) has rapidly become a cornerstone of modern business operations, offering scalable solutions, simplified maintenance, and reduced upfront costs. Yet as SaaS adoption soars, security concerns surrounding these cloud‑based applications also grow increasingly pressing.
With critical data stored on third‑party servers, organizations must remain vigilant about unauthorized access, misconfigurations, and compliance missteps. Failing to address these security risks can lead to devastating outcomes including data breaches, reputational damage, and regulatory fines.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the most common SaaS security vulnerabilities, why they matter, and provide actionable solutions to safeguard your cloud environments. Whether you’re new to SaaS software or managing multiple platforms, this guide offers practical insights into building a robust security strategy.
For additional context on the digital transformation journey, check out our insights on what is digital transformation.

Understanding SaaS security concerns is critical in today’s cloud‑driven world. SaaS applications offer incredible benefits in terms of scalability and cost‑effectiveness; however, they also bring unique challenges that stem from storing and processing data on third‑party servers. In this section, we define SaaS security concerns and explain why it is essential for organizations to not only rely on their providers but also implement their own security measures. The shared responsibility model means that while the provider secures the underlying infrastructure, customers must ensure proper configuration and access control. To learn more about the evolution of cloud services, visit our article on what is SaaS.
SaaS security concerns refer to the challenges and vulnerabilities inherent in cloud‑based software applications. These issues arise because the critical data of an organization is stored, processed, and managed by a third‑party provider—outside the traditional network perimeter. Unlike on‑premises deployments, SaaS security relies on both the vendor's measures and the customer's configuration practices to safeguard sensitive data. A failure in either area can result in severe security breaches.
The primary risks associated with SaaS security include:
Access Control and Security Risks: Unauthorized access can occur if user credentials are stolen or poorly managed. Enforcing strong password policies and multi‑factor authentication (MFA) is essential.
For more on compliance challenges, explore our post on SaaS Security Concerns: Risks, Challenges, and Solutions.
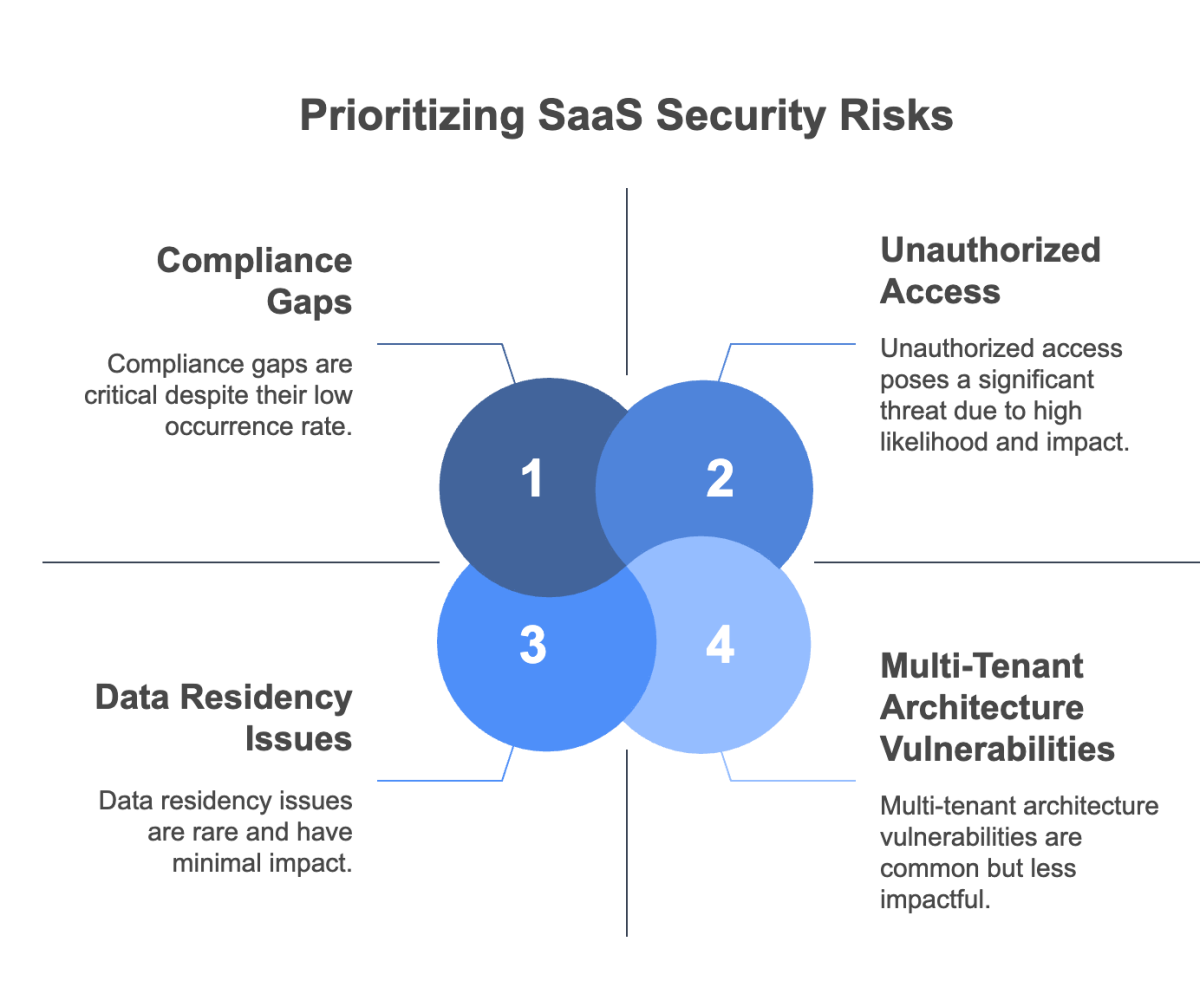

Although SaaS platforms offer significant benefits such as reduced hardware costs and seamless updates, they also introduce considerable risks. These risks arise from the inherent nature of cloud services and the shared responsibility model, where both the provider and the customer play a role in security. In this section, we examine the various risks associated with SaaS platforms and why they demand proactive management. Understanding these risks is the first step toward mitigating potential breaches and ensuring that your data remains secure. For further insights into managing cloud vulnerabilities, see our discussion on SaaS Security Monitoring.
Storing data in a multi‑tenant cloud environment increases the overall attack surface. If one tenant is compromised, there is a risk that attackers may exploit shared resources or vulnerabilities to gain access to data belonging to other tenants.
Cybercriminals often target user credentials, especially those with administrative privileges. Weak passwords, phishing attacks, and the lack of MFA contribute to the risk of account takeovers, which can lead to unauthorized access and data theft.
Adhering to international regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 is challenging in cloud environments. A breach in compliance can result in heavy fines and damage to your company’s reputation.
Vendor lock‑in occurs when organizations become overly dependent on a single SaaS provider, making it difficult to migrate data or switch services without significant disruption and cost. This risk is exacerbated when data formats are proprietary and migration tools are lacking.
Cloud‑native exploits, such as misconfigured IAM services or unpatched APIs, are common. These vulnerabilities can be exploited to bypass security controls and gain unauthorized access, further compounding the risks associated with SaaS platforms.
The consequences of these risks are severe—ranging from financial losses and legal penalties to irreparable damage to your brand’s reputation. A single breach can erode years of trust, emphasizing the critical need for comprehensive security strategies. To learn more about protecting your cloud infrastructure, read our article on SaaS Security Standards and Certifications Explained.
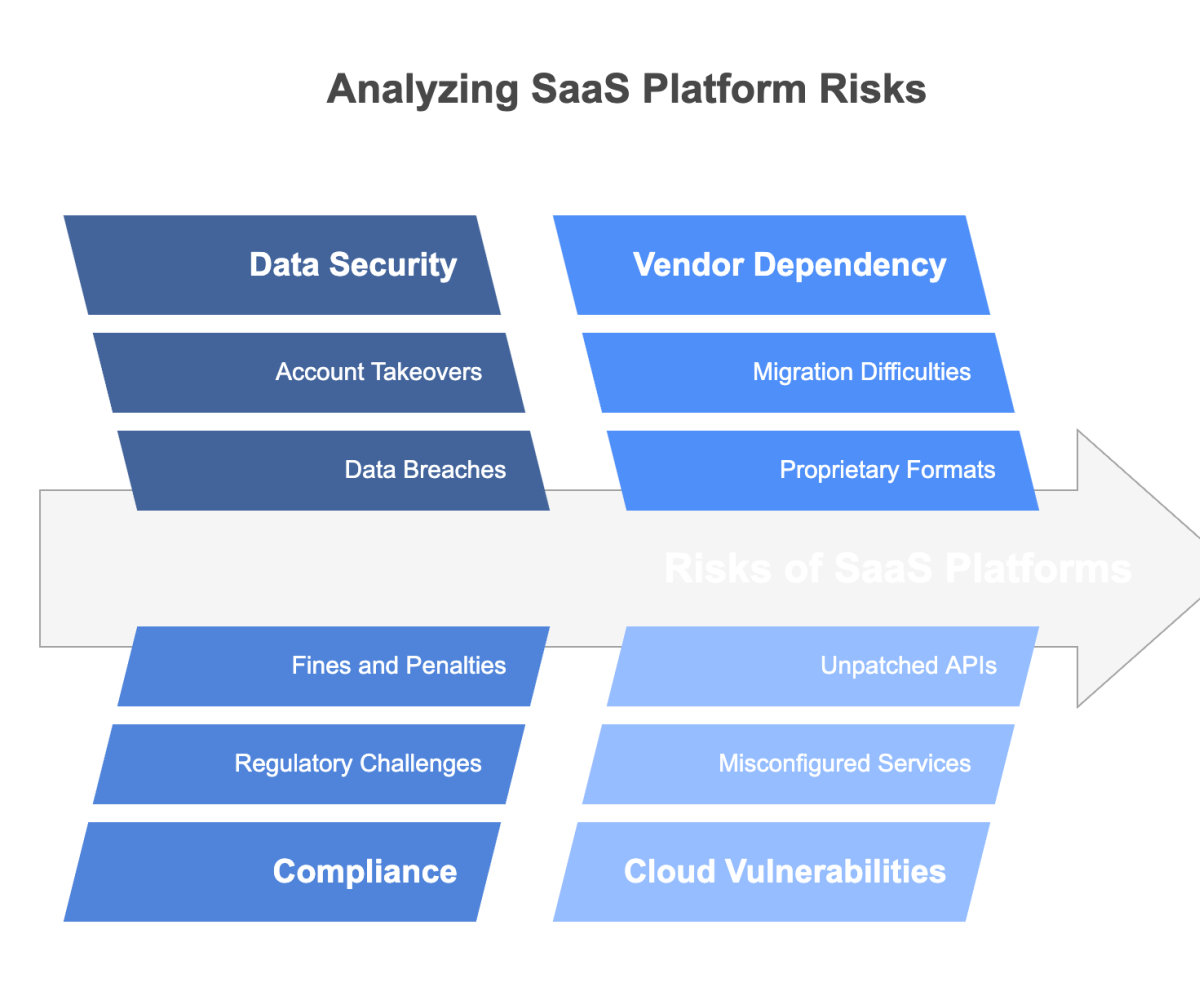

Mitigating SaaS security concerns requires a multi‑layered approach that involves robust technology, comprehensive policies, and continuous monitoring. In this section, we outline several best practices and solutions to manage and reduce the risks inherent in cloud‑based environments.
From implementing strong access controls to adopting AI‑powered security tools, these strategies will help you build a secure and resilient SaaS infrastructure. For a deep dive into effective SaaS security tools, check out our post on Choosing the Right SaaS Security Tools.
Deploying robust access controls is fundamental to protecting SaaS environments. This includes enforcing multi‑factor authentication (MFA), implementing role‑based access control (RBAC), and ensuring that Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions are in place. These measures significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. For example, using SSO with MFA can help safeguard critical systems even if a password is compromised.
Continuous security monitoring is essential for detecting anomalies and potential breaches in real time. Tools such as SIEM systems enable organizations to aggregate logs and set automated alerts for suspicious activities. This proactive approach helps prevent small issues from escalating into major security incidents. To explore real‑time monitoring solutions, read our guide on SaaS Security Monitoring.
Ensure that your SaaS providers adhere to necessary security standards by regularly reviewing their compliance certifications and audit reports. Request updates on frameworks like SOC 2, GDPR, and ISO 27001. This ongoing evaluation helps confirm that the vendor’s security practices align with your compliance needs and reduces the risk of unexpected vulnerabilities.
A well‑defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing damage in the event of a security breach. This plan should outline clear procedures for identifying, containing, and remediating incidents. Regular drills and updates to the plan ensure that your team is prepared to respond quickly and effectively, reducing the potential impact of any breach.
As threats become more sophisticated, AI‑powered security tools offer significant advantages by detecting anomalies and automating responses. These tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns indicative of a breach, enabling faster containment and mitigation. For insights into AI‑driven security, see our article on Understanding AI SaaS Companies.
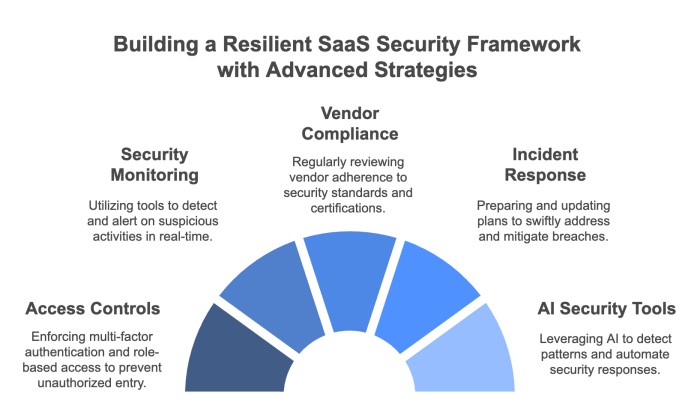

Addressing the multifaceted challenges of SaaS security requires a range of solutions that target different aspects of the security landscape. In this section, we detail several key solutions that organizations can deploy to protect their SaaS environments.
These include advanced identity and access management, continuous security monitoring, robust encryption methods, and the development of a comprehensive SaaS security strategy. Each solution is designed to address specific vulnerabilities while also providing a layered defense that minimizes the overall risk.
To see how these solutions integrate with digital transformation strategies, check out our article on How to Build a Successful SaaS Business Model.
Implementing effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) is vital for preventing unauthorized access. By centralizing control over user credentials, employing Multi‑Factor Authentication (MFA), and enforcing Role‑Based Access Control (RBAC), you can ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data. IAM solutions can also provide detailed audit logs to track user activity, helping to identify and respond to potential breaches quickly.
Continuous security monitoring tools are essential for real‑time threat detection and incident response. These tools aggregate data from various sources, including application logs, network traffic, and user activities, and analyze them for anomalies. This proactive approach enables your security team to detect suspicious behavior immediately and take corrective action before a breach escalates. Learn more about proactive monitoring in our post on SaaS Security Monitoring.
Robust encryption and secure data storage are the cornerstones of protecting sensitive information in SaaS environments. Encryption should be implemented both for data at rest and in transit using industry‑standard protocols. Additionally, ensure that your provider offers strong data storage measures such as redundant backups and disaster recovery plans. For a detailed look at data protection strategies, visit our article on SaaS Data Ownership and Portability.
A comprehensive security strategy goes beyond deploying individual tools; it involves creating and enforcing a set of policies that govern all aspects of your SaaS environment.
This includes regular security audits, employee training programs, incident response planning, and continuous risk assessments.
Integrating these practices helps maintain a secure posture even as your business scales and new threats emerge. For more on creating secure strategies, read our insights on SaaS Security Concerns.

Below are some frequently asked questions regarding SaaS security, along with detailed answers to guide your security strategy. These insights are designed to help you understand common challenges, evaluate the effectiveness of various solutions, and implement best practices tailored to your organization’s needs.
SaaS security concerns encompass issues such as data breaches, unauthorized access, compliance failures, and vulnerabilities in multi‑tenant environments. These challenges arise because sensitive data is managed by third‑party providers, making it critical for organizations to implement robust access controls and continuous monitoring.
Businesses can mitigate risks by enforcing strong access controls (including MFA and RBAC), deploying continuous monitoring tools, and conducting regular vendor audits. Training employees on security best practices is also essential. For a detailed overview of risk mitigation strategies, check our post on SaaS Security Monitoring.
The main challenges include managing data breaches in multi‑tenant environments, ensuring continuous compliance with evolving regulations, and preventing account takeovers. Additionally, vendor lock‑in and securing third‑party integrations can further complicate the security landscape.
Reputable SaaS providers invest in advanced encryption, continuous patching, and robust infrastructure security. They also undergo independent audits such as SOC 2 and ISO 27001. However, customers must configure access controls and monitor usage to complement these measures.
Tools like Datadog, Vanta, and Microsoft Cloud App Security provide automated real‑time monitoring, threat detection, and compliance reporting. These solutions help reduce the manual burden on security teams while ensuring a proactive defense strategy.

Compliance in a SaaS environment is complex due to diverse regulatory requirements and the shared responsibility model. Organizations must ensure that both the SaaS provider and the customer adhere to necessary standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001. This section outlines best practices to maintain compliance while managing SaaS security risks.
From conducting vendor risk assessments to implementing robust data retention policies, these measures ensure your organization stays on the right side of the law while protecting sensitive data. For further insights on compliance, visit our guide on SaaS Security Standards and Certifications Explained.

SaaS platforms have revolutionized business operations by offering scalable and cost‑effective solutions. However, this convenience comes with significant security risks that must be proactively managed. From data breaches and compliance failures to account takeovers and vendor lock‑in, the challenges are complex but not insurmountable.
By adopting robust security practices—such as strong access controls, continuous monitoring, encryption, and comprehensive compliance strategies—organizations can significantly reduce these risks and safeguard their critical data. Embracing a layered security strategy and leveraging advanced tools is not just a best practice; it’s a strategic imperative in today’s digital landscape. For more guidance on building a secure cloud environment, read our related article on SaaS Management Platforms: Do You Need One?.

Ready to take your SaaS security strategy to the next level? Download our free eBook, "SaaS Security Unmasked", for a comprehensive guide on:
Equip your organization with the knowledge to protect your cloud‑based services and ensure a robust security posture. Don’t let security vulnerabilities undermine your business—download our eBook now.
For additional insights on SaaS security and effective cloud risk management, explore these related articles: