
Wednesday, February 5, 2025
Kevin Anderson
As cloud computing becomes the backbone of modern business, Software as a Service (SaaS) stands out as one of the most transformative delivery models for software solutions. Instead of installing applications on individual workstations or managing complex on-premise servers, organizations can access web-based software hosted by a SaaS provider. This setup—the SaaS environment—offers subscription-based access, managed hosting, and simplified maintenance, ensuring that businesses of all sizes can quickly deploy the tools they need.
This article delves into what is a SaaS environment, explores its key features, highlights productivity benefits, and shows why B2B SaaS applications have become essential for enterprise software deployments. We’ll also answer common questions about how SaaS differs from traditional hosting, discuss multi-tenancy in SaaS environments, and outline emerging trends shaping the future of this model.

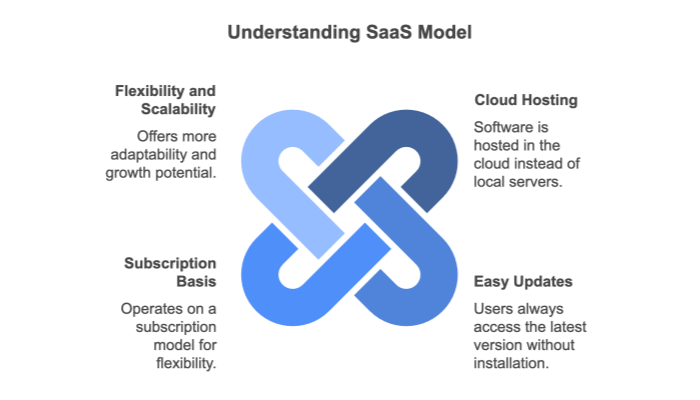
A SaaS environment refers to a cloud-based SaaS system where software applications are hosted and maintained by a third-party provider, then delivered to customers over the internet. Businesses and individual users can access these applications through a browser or lightweight client, paying through a subscription model—often monthly or annually—instead of purchasing a perpetual license.
In simpler terms, “SaaS is a cloud hosting environment that offers” on-demand access to software without the need for substantial upfront investments. This environment is designed to handle updates, patches, security, and scaling on behalf of the customer, freeing companies to focus on their core operations rather than IT infrastructure. Common examples include customer relationship management (CRM) systems, collaboration tools, and office productivity suites, all maintained by SaaS providers.
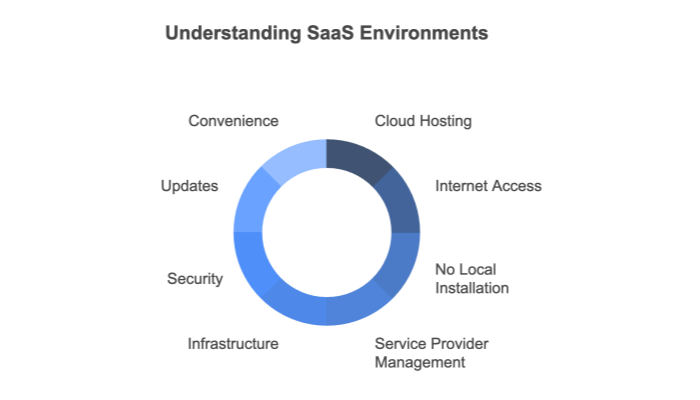

A SaaS environment is a cloud-based model where software applications are hosted and managed by a provider, allowing users to access them via the internet. This eliminates the need for on-premise installations, offering scalability, automatic updates, and seamless accessibility.
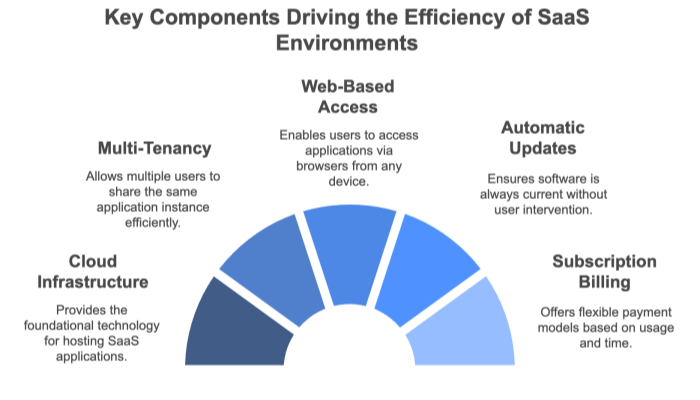
SaaS providers host applications on remote servers. These servers can be physical machines or virtual machines running in massive data centers. The infrastructure is optimized for continuous availability and automated failover.
Multi-tenancy in SaaS environments means a single application instance can serve multiple customers, or “tenants,” simultaneously. Each tenant’s data remains segregated and secure, while the underlying codebase and server resources are shared for efficiency.
Users typically log in through a web browser, removing the need for complex installations or hardware configurations. Some SaaS solutions also provide desktop or mobile clients, but the core functionality resides in the cloud.
Software patches, feature enhancements, and security fixes are implemented by the vendor. Customers always have access to the latest version, eliminating the burden of manual upgrades.
Instead of paying a large upfront fee for a perpetual license, customers usually subscribe to the service monthly or yearly. Usage-based billing models—charging by the number of users or transactions—are also common.
For instance, Microsoft 365 and Slack are SaaS products that streamline communication and productivity, offering robust tools accessible from anywhere.
In traditional hosting, businesses purchase licenses, set up servers, and manage deployments themselves. With SaaS, the provider assumes these responsibilities, offering a managed hosting experience and delivering software as an on-demand service.

Ease of access, lower capital costs, fast deployment, and automatic updates top the list. Multi-tenancy and on-demand scalability also help businesses stay agile and competitive.
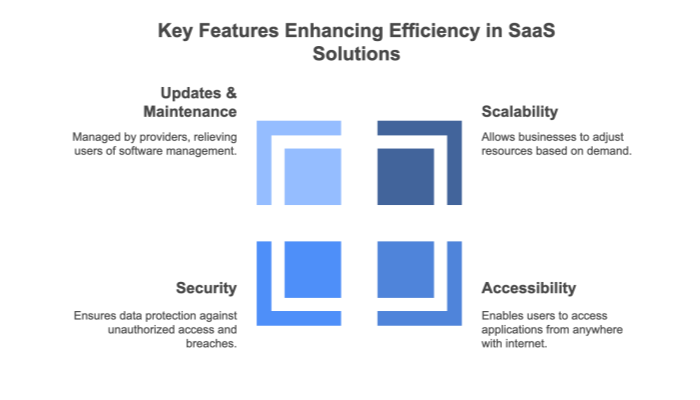

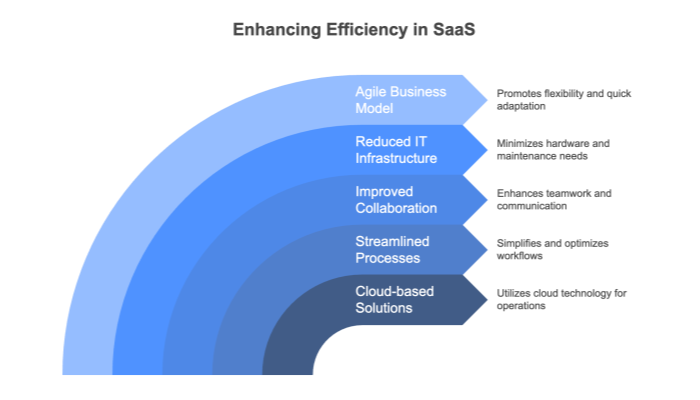
One of the core advantages of adopting a cloud-based SaaS system is its potential to boost efficiency across various organizational processes. From simplified software management to real-time collaboration, SaaS environments can transform how teams operate.
While the exact gains vary, studies often report a 15–40% boost in efficiency due to reduced manual tasks, quicker updates, and enhanced collaboration.

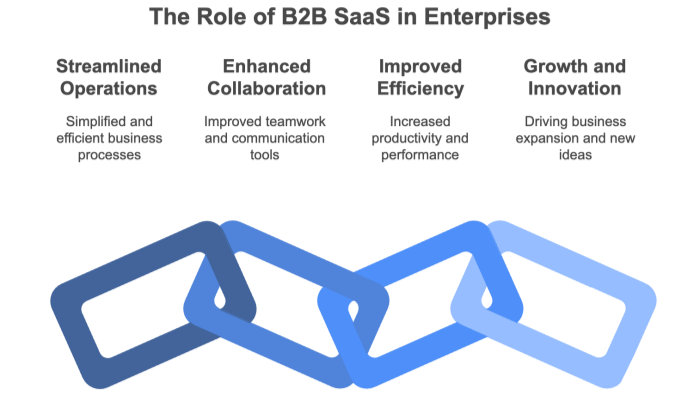
B2B SaaS (Business-to-Business Software as a Service) provides cloud-based solutions tailored for enterprises, streamlining operations across various departments. From CRM and ERP systems to project management, cybersecurity, and data analytics, B2B SaaS enhances efficiency, collaboration, and decision-making for businesses of all sizes.
A B2B SaaS environment refers to enterprise software delivered via the cloud, tailored for business-to-business scenarios. These platforms are designed to handle large volumes of data, complex workflows, and multiple user roles.
Core Components of B2B SaaS:
B2B SaaS Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot, Workday, and SAP Business ByDesign.

SaaS spans various categories, from productivity tools to enterprise-level solutions. Notable examples include:
Common examples include Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace, Slack, Trello, and Dropbox. More specialized offerings include Salesforce for CRM, Shopify for e-commerce, and Workday for HR and financial management.


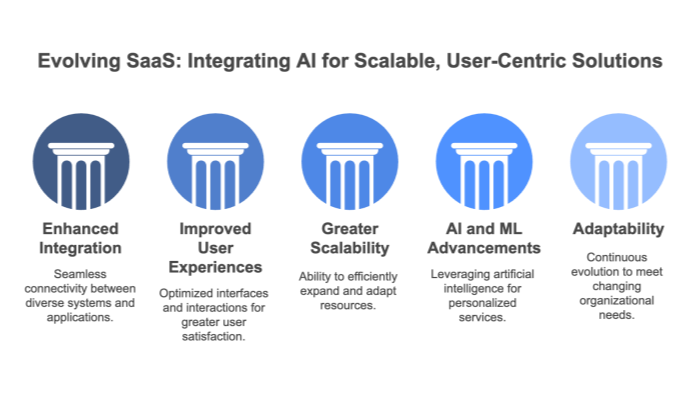
The future of SaaS environments is driven by advancements in AI, automation, and enhanced cloud security. Emerging trends include AI-powered analytics, no-code/low-code platforms, hyper-personalization, and industry-specific SaaS solutions. As businesses prioritize scalability, integration, and data-driven decision-making, SaaS providers will continue to innovate with serverless computing, edge computing, and improved multi-cloud strategies to enhance performance and flexibility
As artificial intelligence matures, SaaS environments increasingly incorporate AI-driven features—from predictive analytics to chatbots. This evolution allows businesses to:
While horizontal SaaS—tools applicable to multiple industries—will remain crucial, there’s growing demand for domain-specialized SaaS that addresses niche processes and compliance requirements. Examples include healthcare EHR systems or retail inventory tools.
As businesses seek faster response times and data governance, hybrid cloud and edge computing will play a role in shaping SaaS. Some providers may offer local data processing combined with cloud-based analytics, minimizing latency and meeting regulatory constraints.
SaaS providers are building deeper personalization into their offerings, whether customizing user interfaces or leveraging machine learning to recommend relevant features based on usage patterns.
Environmental concerns are influencing data center operations. Expect SaaS providers to emphasize energy efficiency, renewable energy usage, and carbon-offset programs to meet customer demand for greener solutions.
AI-driven features, niche vertical solutions, hybrid edge computing, deep personalization, and sustainability initiatives all influence how SaaS is evolving.

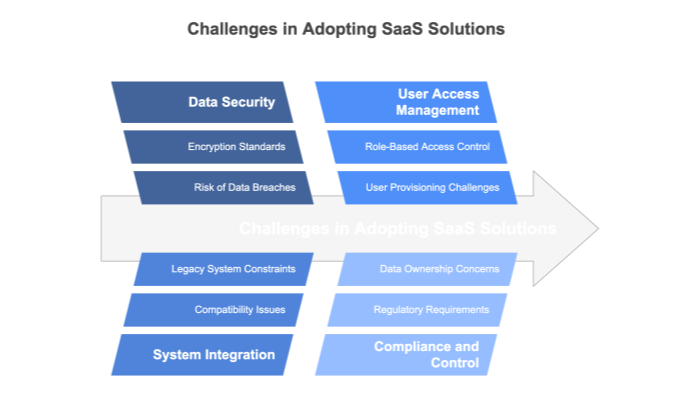
Though the benefits are significant, organizations must also be aware of potential pitfalls when transitioning to a SaaS environment:


A SaaS environment is more than just software accessed through the internet; it’s a comprehensive ecosystem where multi-tenancy, continuous updates, and on-demand scalability revolutionize how businesses adopt and manage technology. By shifting the burden of installation, upgrades, and server maintenance to SaaS providers, organizations can focus on their core objectives—whether that’s driving sales, optimizing workflows, or scaling into new markets.
What is a SaaS environment? At its heart, it’s a cloud-based hosting model that delivers software as a subscription, cutting costs and complexity. From small startups needing quick access to enterprise-grade tools, to large corporations requiring robust B2B integrations, SaaS is a cloud hosting environment that offers remarkable flexibility, resilience, and opportunities for innovation. As technologies like AI, edge computing, and vertical specialization continue to evolve, SaaS environments will remain at the forefront of software delivery—pushing productivity to new heights and redefining how organizations leverage digital solution.
Are you ready to transform your business with SaaS? Learn how to adopt cloud-based solutions effectively and avoid hidden fees, vendor lock-in, and other pitfalls. Our comprehensive eBook, Don’t Get SaaS’d, offers actionable strategies, real-world case studies, and expert insights to help you make informed decisions.