
Sunday, February 2, 2025
Kevin Anderson
The Software as a Service (SaaS) business model has redefined how software is delivered, purchased, and utilized. Unlike traditional software requiring installations and maintenance, SaaS operates through the cloud, providing businesses with seamless access to tools on a subscription basis. This model has become the cornerstone for innovation and scalability, powering startups and enterprises alike.
The SaaS industry has seen exponential growth, projected to reach $720 billion by 2028. Its appeal lies in its flexibility, cost-efficiency, and ability to address modern business challenges. By adopting SaaS, businesses eliminate infrastructure burdens, enhance collaboration, and gain access to cutting-edge technology.
This guide explores the SaaS business model, breaking down its components, benefits, and challenges while highlighting why it has become the gold standard for software delivery in the digital age.

Software as a Service (SaaS) represents a cloud-based delivery model where software applications are hosted online and accessed via a web browser. Unlike traditional software models that require downloads and installations, SaaS operates on the principle of accessibility and subscription-based usage.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, this model has transformed how businesses adopt technology, eliminating the need for cumbersome installations and constant manual updates. Its cloud foundation enables real-time scalability and cost management while reducing IT overhead. Companies can quickly integrate new features, ensure continuous security updates, and remain agile in responding to market shifts.
This seamless integration of technology fosters innovation, simplifies maintenance, and allows organizations to focus on core business objectives. The ease of deployment and regular updates further enhance operational efficiency and user satisfaction, making SaaS a preferred model for companies of all sizes looking to optimize their technology investments.
At its core, SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to manage complex IT infrastructure. Instead, users access the software through the internet, and the provider handles everything from updates to security. This shift simplifies operations, making SaaS an attractive option for startups and established businesses alike.
Example: Platforms like Google Workspace and Slack epitomize SaaS by offering tools accessible anytime, anywhere.

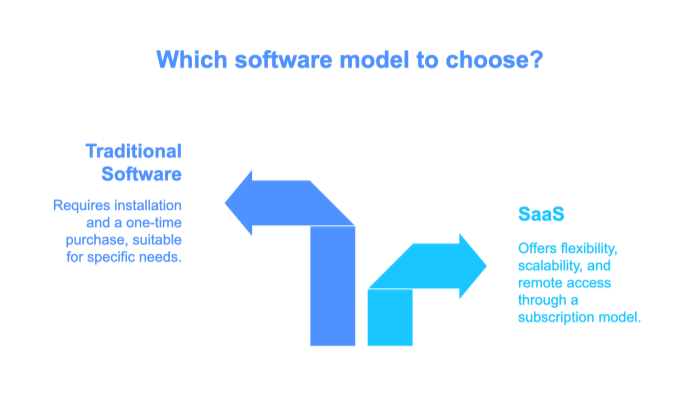
This comparison highlights the fundamental differences between cloud-based SaaS solutions and traditional on-premise software. The SaaS model is centered on delivering software over the internet, which allows for continuous updates and scalability without significant hardware investments. In contrast, traditional software must be installed locally, often leading to higher upfront costs and more complex maintenance routines.
This side-by-side evaluation clarifies operational, financial, and technical differences, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about which model aligns best with their current needs and future growth objectives. By understanding these distinctions, companies can strategically plan their IT investments while balancing cost, efficiency, and flexibility.
| Feature | SaaS | Traditional Software |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery | Cloud-based, accessed online | Installed on individual devices |
| Cost Model | Subscription-based, pay-as-you-go | Upfront licensing fees |
| Updates | Automatic and seamless | Manual and often disruptive |
| Scalability | Easy to scale up or down | Requires additional hardware/software |

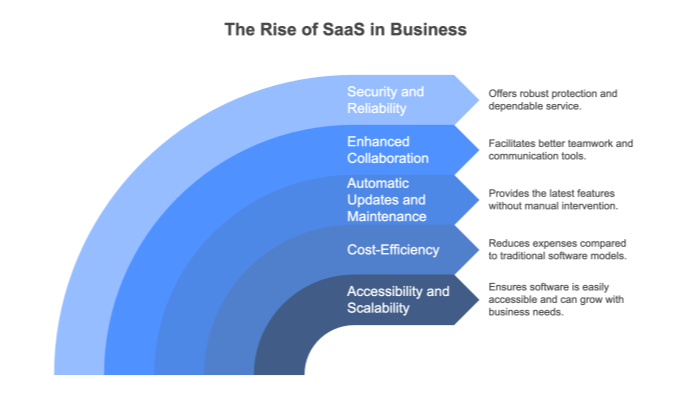
The SaaS business model has become a game-changer for companies across the globe, offering an innovative approach to software delivery. Unlike traditional software models, SaaS provides unparalleled benefits that cater to the fast-paced, ever-changing demands of modern businesses.
From enhanced flexibility to significant cost savings, SaaS empowers organizations to streamline operations and adapt quickly to market demands. Its cloud-based nature means that updates, security patches, and new features are continuously rolled out without disrupting business continuity.
This adaptability not only reduces the burden on IT departments but also fosters an environment of continuous improvement and innovation. As companies increasingly embrace remote and hybrid work models, the accessibility and scalability inherent in SaaS solutions further solidify its dominance in today’s digital economy.
SaaS platforms thrive on their accessibility, enabling businesses to operate from virtually anywhere. With only an internet connection, users can access applications from desktops, laptops, or mobile devices. This flexibility has been pivotal in supporting the rise of remote and hybrid work environments.
SaaS dramatically reduces the financial burden on businesses. Instead of investing heavily in hardware, software licenses, and IT maintenance, companies adopt a subscription-based model that spreads costs over time. This pay-as-you-go approach is especially beneficial for small businesses and startups with limited budgets. Freemium plans and tiered pricing also provide flexibility, allowing companies to pay only for the features they need.
With SaaS, the responsibility for software updates and maintenance lies with the provider. This ensures businesses always have access to the latest features and security patches without experiencing downtime or requiring manual intervention. For example, platforms like Microsoft 365 continuously roll out updates, keeping users productive and secure.
SaaS platforms excel at fostering collaboration, a necessity for businesses with distributed teams. Tools like Slack, Zoom, and Google Workspace enable real-time communication, file sharing, and project management, ensuring teams stay connected and aligned. Features like simultaneous document editing or live video conferencing have redefined how teams collaborate, making workflows more efficient.

Small businesses stand to gain significantly from the SaaS model. Its affordability and ease of implementation make it a natural fit for organizations that lack the resources to manage traditional software systems. By reducing upfront capital expenditure and shifting to a predictable subscription model, SaaS empowers small enterprises to access powerful tools previously reserved for larger companies.
This democratization of technology enables improved efficiency, streamlined operations, and competitive parity with market leaders. With minimal IT infrastructure requirements, SaaS allows businesses to scale as needed while only paying for the services they use. The ability to quickly adopt and integrate new functionalities further supports dynamic business environments, making SaaS an optimal solution for small businesses striving to remain agile and innovative.
SaaS providers invest heavily in robust security measures to protect user data. Features like multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and compliance with regulations such as GDPR provide peace of mind for businesses. Additionally, the reliability of SaaS systems—often boasting 99.9% uptime—ensures uninterrupted operations.
SaaS has also evolved to cater to niche industries through vertical SaaS solutions. These tailored platforms address the unique challenges faced by specific sectors such as healthcare, real estate, or education. For example, healthcare SaaS applications ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA while streamlining patient management systems.

The success of SaaS lies not only in its innovative delivery model but also in the diverse approaches companies use to cater to their customers. Various SaaS business models have emerged to meet different market needs, each designed with unique pricing structures, levels of service, and customer engagement strategies.
By understanding these models, businesses can select the framework that best aligns with their operational goals and customer base.
This exploration of models offers insight into how companies structure revenue, manage customer relationships, and plan for scalability, ultimately positioning themselves for sustainable growth in a competitive market.
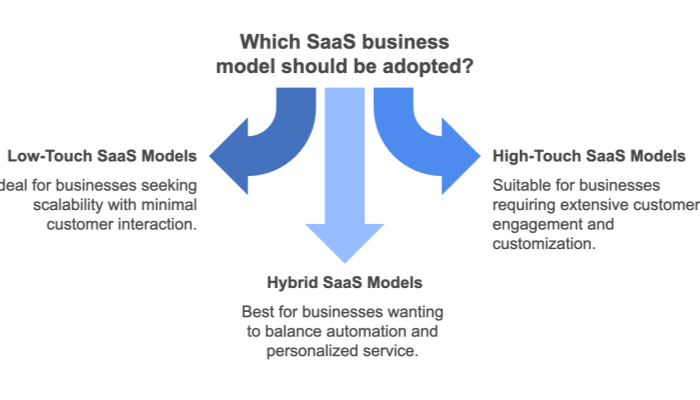
Low-touch SaaS focuses on simplicity, automation, and self-service. These models are designed for products that require minimal human interaction during the sales and onboarding processes. Customers typically discover, evaluate, and purchase the software through a website, often supported by free trials or freemium models.
Characteristics:
High reliance on automation for onboarding and customer success.
Scalable pricing plans, appealing to both individuals and small businesses.
Limited customer support, often supplemented with knowledge bases or tutorials.
Examples:
Trello: A visual project management tool offering intuitive self-service onboarding.
Basecamp: A collaboration platform with minimal setup requirements, ideal for small teams.
Advantages:
Lower customer acquisition costs (CAC) due to minimal human involvement.
Scalable revenue models that cater to a broad customer base.
In contrast, high-touch SaaS models are designed for enterprise customers who require personalized support and tailored solutions. These models involve a human-intensive process, with dedicated sales and customer success teams working closely with clients throughout the sales journey.
Characteristics:
Customized pricing and contracts based on client requirements.
Strong emphasis on relationship-building and account management.
Complex onboarding processes supported by dedicated teams.
Examples:
Salesforce: A CRM giant that offers comprehensive enterprise solutions with a high degree of customization.
SAP: Provides industry-specific ERP solutions for large-scale enterprises.
Advantages:
High revenue per customer due to enterprise-level pricing.
Strong customer retention through relationship-driven strategies.
Hybrid SaaS combines elements of low-touch and high-touch models, allowing companies to cater to both small businesses and enterprises. This approach is particularly useful for SaaS platforms that serve diverse customer bases with varying levels of needs.
Characteristics:
Freemium or self-service options for smaller customers.
Dedicated account managers and premium features for enterprise clients.
Flexible pricing tiers that accommodate different use cases.
Examples:
HubSpot: Offers free CRM tools with advanced marketing and sales features available for premium customers.
Zoom: Provides free basic plans while offering enterprise-level solutions for larger organizations.
Advantages:
Ability to scale revenue streams by addressing multiple market segments.
Balance between automation and personalized service.

SaaS businesses generate revenue through various mechanisms, each tailored to maximize customer value and profitability. This multi-faceted revenue approach allows companies to choose models that best suit their product offerings and target markets.
By leveraging recurring payments, usage-based fees, and tiered service levels, SaaS providers can maintain steady cash flow while offering flexibility to their customers.
These revenue streams not only support continuous innovation but also provide the financial stability needed for scaling operations, investing in technology, and enhancing customer experience.

Success in SaaS relies heavily on tracking and optimizing key performance indicators (KPIs) that offer insights into operational efficiency and growth potential. These metrics serve as a vital dashboard for monitoring revenue consistency, customer engagement, and the overall financial health of the business.
By focusing on quantifiable targets, companies can pinpoint areas that require improvement and strategize on scaling their operations. The alignment of these metrics with business goals fosters data-driven decision-making and long-term planning, ensuring that every aspect of the SaaS model contributes to sustainable success.
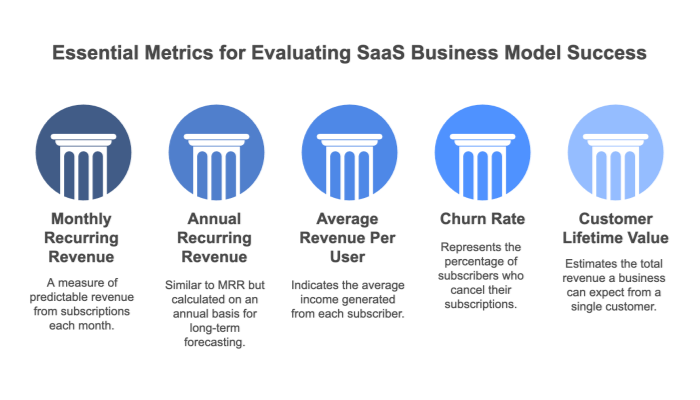
MRR represents the predictable revenue generated from subscriptions each month. It’s one of the most critical metrics for SaaS businesses as it directly reflects the company’s growth trajectory.
How to Calculate:
MRR = Total Active Customers × Average Revenue Per User (ARPU).
Why It Matters:
Tracks revenue consistency.
Helps forecast future income.
ARR is a broader metric that projects yearly revenue from subscriptions, offering a long-term view of revenue potential for enterprise-focused SaaS businesses with annual contracts.
How to Calculate:
ARR = MRR × 12.
Why It Matters:
Measures long-term revenue potential.
Facilitates growth comparisons over multiple years.
ARPU measures the revenue generated per customer in a specific period, helping SaaS businesses understand customer value.
How to Calculate:
ARPU = Total Revenue / Total Customers.
Why It Matters:
Evaluates the effectiveness of upselling and cross-selling strategies.
Highlights opportunities to increase pricing tiers.
Churn measures the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions during a given period. A high churn rate can severely impact revenue and growth.
How to Calculate:
Churn Rate = (Customers Lost During Period / Total Customers at Start of Period) × 100.
Why It Matters:
Indicates customer satisfaction.
Helps assess the need for retention strategies.
CLV represents the total revenue a business expects to earn from a customer over their entire relationship.
How to Calculate:
CLV = (ARPU × Average Customer Lifetime in Months) - Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
Why It Matters:
Informs decisions on customer acquisition spending.
Highlights the importance of retention.
NRR reflects the revenue retained from existing customers, including expansions, upgrades, and downgrades.
How to Calculate:
NRR = (Starting Revenue + Expansion Revenue - Churn Revenue) / Starting Revenue × 100.
Why It Matters:
Demonstrates the effectiveness of upselling strategies.
Indicates overall customer satisfaction.
CAC measures the cost of acquiring a single customer. Lowering CAC while maintaining high customer value is a key goal for SaaS businesses.
How to Calculate:
CAC = Total Sales and Marketing Expenses / Total New Customers Acquired.
Why It Matters:
Determines the efficiency of marketing efforts.
Affects overall profitability.
This metric shows how long it takes to recover the cost of acquiring a customer.
How to Calculate:
CAC Payback Period = CAC / Monthly Gross Margin per Customer.
Why It Matters:
Indicates how quickly a SaaS business can recoup its investments.
Helps assess cash flow management.
Gross margins measure the profitability of a SaaS business after accounting for the costs of delivering the service (e.g., server costs, customer support).
How to Calculate:
Gross Margin = (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue × 100.
Why It Matters:
Shows operational efficiency.
Impacts long-term financial health.
Logo churn measures the percentage of customers lost during a specific period, regardless of their revenue contribution.
Why It Matters:
Highlights the need for retention efforts.
Tracks customer satisfaction trends.
Revenue churn focuses on the revenue lost from customer cancellations rather than the number of customers.
Why It Matters:
Provides a clearer picture of financial impact.
Helps prioritize retention strategies for high-value customers.
Tracking and optimizing these metrics is essential for driving growth, improving customer satisfaction, and ensuring the long-term success of a SaaS business. By focusing on key indicators like MRR, churn rate, and CAC, businesses can make data-driven decisions that lead to sustainable profitability and scalability.

While the SaaS business model offers significant advantages, it also presents unique challenges and risks that businesses must address to achieve sustainable success. Navigating issues related to security, customer retention, and cost management is essential to maintain service quality and operational efficiency. Providers face obstacles such as data breaches, integration complexities, and rapidly shifting market expectations.
Understanding these challenges in depth helps companies develop robust mitigation strategies that safeguard both operational integrity and customer trust. A proactive approach to risk management not only minimizes potential disruptions but also enhances competitive advantage in an increasingly crowded digital marketplace.
SaaS platforms operate on cloud infrastructure, which introduces security and privacy concerns for businesses and users. Data breaches, misconfigurations, and shared responsibility models are common challenges.
In multi-tenant SaaS architectures, multiple customers share the same infrastructure. While data is logically separated, vulnerabilities can still arise.
Example: A poorly configured security protocol could expose sensitive customer data.
Mitigation Strategies:
Implement advanced encryption (both at rest and in transit).
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance user access security.
Regularly audit systems to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
Switching SaaS providers can be challenging due to proprietary systems, data formats, and lack of portability.
Key Issues:
Businesses may face difficulties exporting data to migrate to another platform.
Dependency on specific SaaS solutions can hinder flexibility in adopting new technologies.
Mitigation Strategies:
Prioritize SaaS platforms with open APIs and clear data portability policies.
Include exit clauses in contracts to ensure smooth transitions if necessary.
High churn rates can severely impact the financial health of a SaaS business. Retaining customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones, making churn management a critical focus.
Factors Contributing to Churn:
Poor onboarding experiences.
Lack of customer support or success programs.
Misalignment between product features and customer needs.
Mitigation Strategies:
Invest in customer success teams to improve onboarding and user satisfaction.
Use predictive analytics to identify at-risk customers and proactively address their concerns.
Regularly update features based on user feedback.
While SaaS models are cost-effective for customers, managing operational costs can be challenging for providers, especially during the growth phase.
Key Challenges:
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Balancing high upfront marketing and sales costs with long-term customer value.
Infrastructure Costs: Scaling server capacity and maintaining uptime for a growing customer base.
Mitigation Strategies:
Optimize marketing strategies to lower CAC while improving customer acquisition.
Leverage cost-efficient cloud providers for scalable infrastructure.
Implement usage-based pricing models to balance revenue against operational costs.
Many businesses rely on a mix of software solutions, requiring SaaS platforms to integrate seamlessly with existing systems.
Key Issues:
Lack of compatibility with legacy systems.
Complex integration processes causing delays and disruptions.
Mitigation Strategies:
Opt for SaaS platforms with robust integration capabilities and open APIs.
Use middleware tools to bridge gaps between incompatible systems.
As the SaaS market becomes increasingly competitive, businesses must continually evolve to meet rising customer expectations.
Challenges:
Delivering consistent, high-quality experiences across diverse customer segments.
Staying ahead of competitors by introducing innovative features.
Mitigation Strategies:
Regularly conduct market research to understand customer needs.
Invest in innovation and R&D to differentiate offerings from competitors.
SaaS providers often operate across multiple regions, requiring compliance with various regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
Key Issues:
Adhering to data residency requirements.
Ensuring user data privacy and security compliance.
Mitigation Strategies:
Partner with legal experts to ensure compliance across jurisdictions.
Regularly update policies and practices to align with evolving regulations.
Addressing these challenges is essential for building a resilient SaaS business. By prioritizing security, managing churn, and optimizing costs, SaaS providers can overcome risks and focus on delivering value to customers. Businesses that proactively tackle these obstacles will position themselves for long-term success in the competitive SaaS market.


The Software as a Service (SaaS) industry continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in technology, changing customer expectations, and the increasing need for flexible, scalable solutions. Emerging trends are redefining the market, as providers incorporate innovative technologies and sustainable practices into their offerings.
This forward-looking approach not only enhances the overall user experience but also helps businesses stay competitive in an ever-changing digital landscape. As organizations seek to streamline operations and harness data-driven insights, these trends offer a glimpse into the future of software delivery.
Embracing these innovations will empower companies to optimize performance, improve security, and foster greater collaboration, thereby reinforcing SaaS as a critical driver of business success.
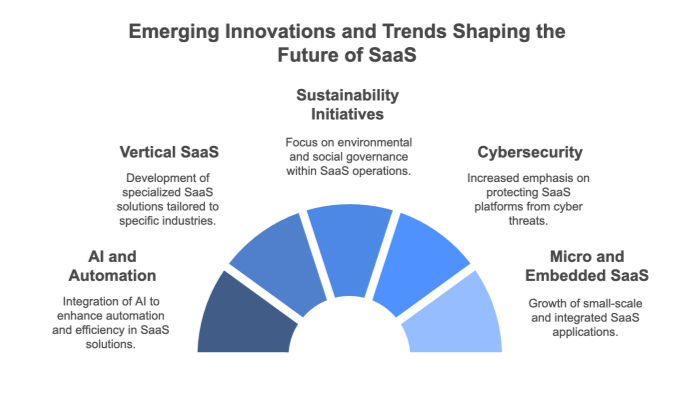
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are revolutionizing SaaS platforms, enabling businesses to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and make data-driven decisions.
Key Innovations:
Predictive Analytics: SaaS platforms now use AI to analyze historical data and predict trends, helping businesses make informed decisions.
Example: CRMs like HubSpot suggest the best times to engage customers based on previous interactions.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Automation is improving customer service by handling routine inquiries and providing instant responses.
Benefits:
Improved operational efficiency through task automation.
Enhanced personalization in customer interactions.
Vertical SaaS platforms cater to the specific needs of industries like healthcare, real estate, and retail. Unlike horizontal SaaS solutions, which serve a broad audience, vertical SaaS focuses on niche markets with tailored features.
Examples of Vertical SaaS:
Healthcare: Platforms like Veeva Systems streamline patient management and ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Retail: Tools like Shopify Plus provide advanced e-commerce features for large-scale retail businesses.
Why It Matters:
Addresses industry-specific challenges with customized solutions.
Increases customer loyalty through specialized features.
As businesses become more environmentally conscious, SaaS providers are adopting sustainability practices to reduce their ecological footprint.
Key Trends:
Green Data Centers: SaaS companies are transitioning to energy-efficient data centers powered by renewable energy.
Example: Google Cloud operates carbon-neutral data centers to minimize environmental impact.
Eco-Friendly Design: SaaS platforms are being optimized to reduce energy consumption during operation.
Benefits:
Enhances brand reputation by aligning with customer values.
Reduces operating costs through energy-efficient technologies.
With the growing reliance on cloud-based platforms, cybersecurity is a top priority for SaaS providers. Ensuring data protection and compliance with regulations is critical to building customer trust.
Emerging Trends:
Zero-Trust Security Models: Requires verification for every access request, minimizing the risk of breaches.
Data Privacy Enhancements: SaaS providers are integrating privacy-first features to comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
AI-Powered Threat Detection: Advanced algorithms identify and neutralize threats in real time.
Micro SaaS refers to small-scale SaaS products created by individuals or small teams. These solutions target niche markets and offer focused functionality.
Characteristics of Micro SaaS:
Simple, single-feature tools addressing specific problems.
Low operational costs, often managed by a single developer.
Examples:
Buffer: Initially a simple social media scheduling tool, it gained traction as a focused micro SaaS product.
Why It’s Growing:
Provides opportunities for solopreneurs to enter the SaaS market.
Addresses underserved niche audiences with precision.
Embedded SaaS integrates directly into other applications or platforms, providing seamless functionality without requiring users to switch tools.
Examples:
Payment gateways like Stripe embed within e-commerce platforms to streamline transactions.
Twilio integrates communication APIs into existing systems, enabling businesses to add messaging and calling features.
Benefits:
Simplifies workflows by consolidating tools.
Improves user experience through seamless integration.
SaaS platforms are leveraging AI to offer highly personalized experiences, tailoring features and recommendations to individual users.
Applications:
Dynamic Dashboards: Customizing interfaces based on user preferences and behavior.
Intelligent Recommendations: Suggesting relevant features, tools, or content to enhance user engagement.
Impact:
Boosts user satisfaction and retention.
Increases adoption of advanced features through targeted suggestions.
As hybrid work becomes the norm, SaaS collaboration tools are evolving to support distributed teams more effectively.
Key Developments:
Real-Time Collaboration: Tools like Slack Huddles and Zoom are adding features to enhance real-time interactions.
Integrated Workflows: Platforms are consolidating features like project management, file sharing, and communication into unified systems.
Why It’s Important:
Keeps remote teams connected and productive.
Reduces tool fatigue by offering all-in-one solutions.
The future of SaaS is defined by innovation, adaptability, and customer-centricity. Businesses that stay ahead of these trends—by integrating AI, adopting sustainable practices, and leveraging vertical SaaS solutions—will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly digital world. As technology evolves, SaaS will remain a cornerstone of business success, driving efficiency and growth across industries.

The SaaS business model has fundamentally reshaped how software is delivered, accessed, and utilized, offering businesses an unparalleled blend of scalability, cost-efficiency, and innovation. From simplifying operations to enabling remote collaboration and providing industry-specific solutions, SaaS continues to dominate as the preferred choice for organizations of all sizes.
Its dynamic nature, combined with a focus on continuous improvement and customer-centric strategies, enables companies to remain competitive while efficiently managing resources and operational challenges. The model’s ability to drive digital transformation and foster innovation is evident across various industries, making it a key enabler of modern business practices.
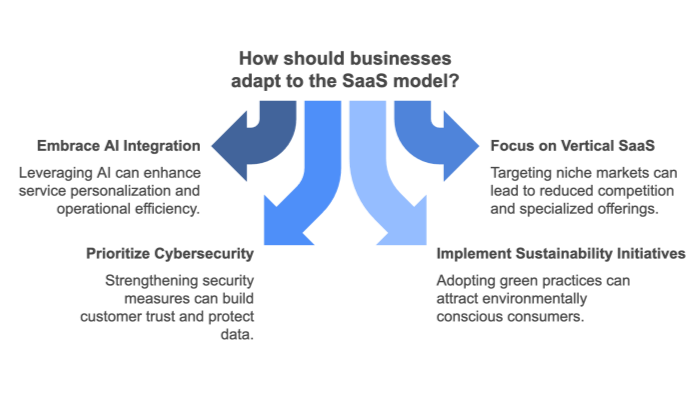
Evaluate SaaS Readiness: Assess your organization’s current software needs and identify areas where SaaS solutions can drive efficiency.
Choose the Right Providers: Focus on platforms that align with your goals, offer robust security, and support seamless integrations.
Monitor Performance: Regularly analyze metrics to refine your strategy and ensure long-term success.
Stay Ahead of Trends: Embrace emerging SaaS technologies like AI and embedded solutions to maintain a competitive edge.

Ready to unlock the full potential of SaaS for your business? Download our eBook: “Don’t Get SaaS’d – A B2B Buyer’s Guide” to explore:
- Strategies for selecting the best SaaS platforms.
- Detailed insights on mitigating risks and maximizing ROI.
- Actionable tips for scaling your business with SaaS.
Equip your business with the knowledge and tools to thrive in the SaaS-driven digital landscape.
