SaaS Data Ownership and Portability: Don’t be a Vendor Hostage
Modern businesses rely heavily on Software‑as‑a‑Service (SaaS) solutions for everything from customer relationship management (CRM) and financial analytics to marketing automation and HR. By delivering software over the cloud through subscription plans, SaaS vendors eliminate much of the infrastructure burden that on‑premise solutions impose. Yet, beneath the convenience and flexibility lies a potential pitfall: SaaS data ownership.
How do you keep full control of your own information when it’s stored on a third party’s servers? What happens if your SaaS provider changes prices or suddenly discontinues a product feature you depend on? Or worse—what if they decide to lock you out entirely, leaving your mission‑critical data trapped in a proprietary format?
This post delves into these crucial issues, showing you how to preserve data portability in SaaS environments, secure your compliance needs, and prevent vendor lock‑in. Drawing on lessons from the eBook Escape the SaaS Trap, it provides insights on negotiating contracts and maintaining control over your data.
Table of Contents
Navigate through the article using the links below:
- Why SaaS Data Ownership Matters
- Common Pitfalls Undermining Data Ownership
- The Role of “Smart SaaS” Certification
- Contract Clauses for Data Ownership and Portability
- Best Practices for Data Control in a SaaS Environment
- Avoiding SaaS Vendor Lock-In: Integration and Openness
- Real-World Examples: Data Ownership Pitfalls and Successes
- Combining Data Ownership with Security and Compliance
- Conclusion: Take Control of Your SaaS Data—Don’t Be a Hostage
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

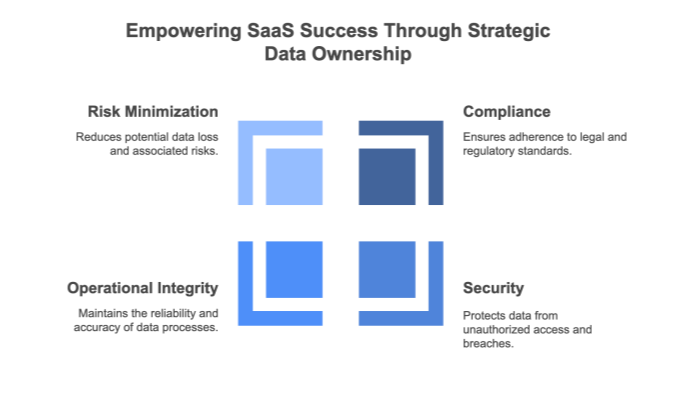
1. Why SaaS Data Ownership Matters
SaaS data ownership is a critical issue for any organization leveraging cloud‑based applications. In this section, we explore the reasons why retaining control over your data is essential. As companies shift to SaaS models, they often relinquish direct control over their data by storing it on external servers. This can expose them to significant risks such as vendor lock‑in, where migrating away from a provider becomes a complex and costly process.
Moreover, limited control over data formats and export capabilities can hinder integration with other systems or compliance with regulatory frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA. The inability to freely transfer data can restrict business agility and innovation. By understanding the importance of data ownership, organizations can make informed decisions, negotiate better contract terms, and implement backup strategies to safeguard critical information.
1.1 Risk of Lock-In and Restricted Choices
SaaS offers convenience, but vendor lock-in can become a major obstacle if businesses lack control over their data and integrations. Many providers make it difficult to migrate away by offering limited data export options, proprietary file formats, or excessive exit fees. This lack of flexibility can trap businesses into long-term commitments with software that may no longer meet their evolving needs.
- Switch Vendors: Migrating to a new provider can be costly and time-consuming if data export tools are inadequate or if the provider restricts access to critical information.
- Integrate with Other Systems: A lack of open APIs and interoperability can prevent businesses from building a unified ecosystem, leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Protect Sensitive Information: Solely depending on the vendor’s security measures may expose businesses to compliance risks, breaches, or loss of control over proprietary data. Organizations should demand transparency regarding security policies and ensure backup solutions are in place.
1.2 Legal and Compliance Ramifications
As businesses increasingly rely on SaaS for critical operations, legal and compliance risks must be carefully managed. Regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and SOC 2 impose strict guidelines on data ownership, processing, and retrieval. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
- Regulatory Requirements: SaaS providers must clearly define data handling practices to comply with regional and industry-specific regulations. Businesses should ensure their vendor meets compliance standards before committing.
- Data Retrieval: Companies must have the ability to export, modify, or delete records upon request to maintain compliance with data privacy laws. Lack of these controls can result in serious legal infractions.
- Audit Readiness: Regulatory audits require full data traceability and portability. Organizations must confirm that their SaaS provider allows on-demand access to logs, reports, and compliance documentation.
1.3 Exit Strategies and Future-Proofing
A smart SaaS strategy includes planning for long-term flexibility and ease of transition should a business outgrow its current provider. Companies that fail to negotiate data ownership terms upfront may find themselves locked into a platform with no clear exit strategy, increasing operational risk.
- Negotiation Leverage: Having a clear, structured data export process gives businesses an advantage during contract renewals, allowing them to push back on price hikes or restrictive clauses.
- Adopt New Tools Freely: Seamless data portability ensures companies can integrate new SaaS solutions or switch providers without costly disruptions.
- Preserve Historical Insights: Retaining access to past data is critical for long-term analytics, business intelligence, and regulatory compliance. Organizations must ensure they can extract and store historical records independently of their SaaS vendor.
By prioritizing data mobility, integration flexibility, and compliance readiness, businesses can prevent vendor dependency and ensure their SaaS investments remain adaptable and future-proof.

2. Common Pitfalls Undermining Data Ownership
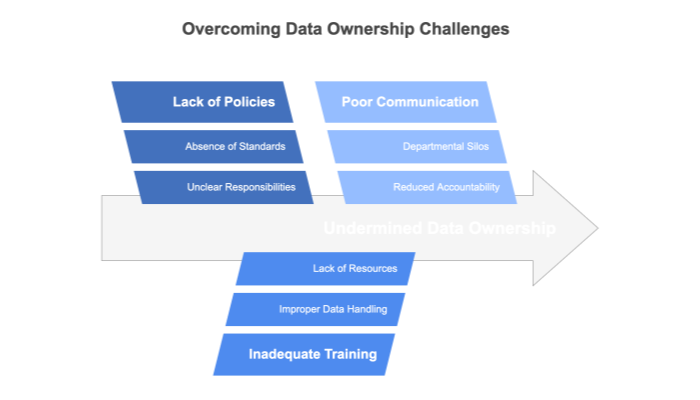
Many organizations become hostage to their SaaS vendors due to unclear data policies and technical limitations. In this section, we detail the common pitfalls that can jeopardize data ownership. These include ambiguous contract language that sounds reassuring but leaves data export methods vague, the use of proprietary data structures that limit portability, and fee-based or restricted export features that add unforeseen costs.
Additionally, some vendors enforce an “all or nothing” approach to data retention, risking permanent loss of data upon termination of service. Finally, insufficient transparency regarding backup and disaster recovery processes can leave your data vulnerable in crisis situations. By identifying these pitfalls, you can proactively negotiate terms that secure your data rights and ensure that you maintain full control over your information.
2.1 Ambiguous Contract Clauses
SaaS contracts often use deceptively reassuring language that gives businesses a false sense of security about their data ownership. However, without clear export policies, retrieval rights, and process details, these clauses can leave organizations vulnerable.
- Vague Wording: Phrases like “customers maintain ownership of their data” sound reassuring but often lack concrete details on how data can be accessed or exported in practice.
- Export Details Missing: Many agreements do not specify data formats, fees for extraction, or time limits for retrieval, leading to confusion or added costs when businesses need to migrate.
To avoid these issues, organizations should demand explicit language in their contracts, clearly outlining data portability rights, accessible formats, and exit procedures before signing.
2.2 Proprietary Data Structures
Some SaaS providers lock customers into their ecosystem by using custom or non-standard file formats that make migration difficult. This tactic forces businesses to either remain with the vendor or invest heavily in manual data conversion when transitioning to a new platform.
- Non-Standard Formats: Data exports may be provided in arcane or vendor-specific formats, preventing seamless integration with other platforms.
- Data Transformation Needed: Businesses often must invest in costly manual processing or develop custom scripts to convert exported data into a usable format.
Organizations should demand industry-standard export formats (CSV, JSON, XML, SQL) and test data retrieval procedures before fully committing to a SaaS provider.
2.3 Limited or Fee-Based Export Features
Even when SaaS providers offer data export functionality, many impose limitations or unexpected costs that make retrieving data cumbersome and expensive.
- Partial Exports: Some vendors restrict access to only certain types of data, preventing businesses from obtaining a complete backup of their records.
- Extra Charges: Large-scale data exports or API-based extractions may incur unexpected high fees, significantly increasing costs for businesses looking to transition.
To prevent these issues, organizations should clarify export options upfront and negotiate unrestricted access to full data sets without incurring excessive fees.
2.4 “All or Nothing” Data Retention
Many SaaS providers enforce strict data deletion policies, meaning that businesses lose access to their information the moment a subscription ends. Without proper planning and timely data exports, organizations risk permanent data loss.
- Short Grace Periods: Some providers delete customer data within days of subscription termination, offering little time for retrieval.
- Risk of Permanent Loss: Without a structured data retention policy, companies may find themselves locked out of crucial business records without a way to recover them.
Organizations should ensure their SaaS contracts include sufficient grace periods for data retrieval and that automated backups are performed before contract termination.
2.5 Weak Transparency on Backups or Disaster Recovery
Backup and disaster recovery (DR) policies should be a critical concern for any business using SaaS. However, many providers fail to disclose details about their backup frequency, storage locations, or data recovery processes, leaving customers uncertain about the safety of their data.
- Unclear DR Processes: Some vendors fail to specify where backups are stored, how often they are updated, or how long they are retained.
- Data Integrity Risks: In the event of data loss, system failure, or cyberattacks, businesses may discover that their backups are outdated or incomplete.
To mitigate these risks, businesses must demand transparency from SaaS providers regarding their backup schedules, retention policies, and recovery time objectives (RTOs). Ensuring independent backup solutions can also provide an added layer of protection.

3. The Role of “Smart SaaS” Certification
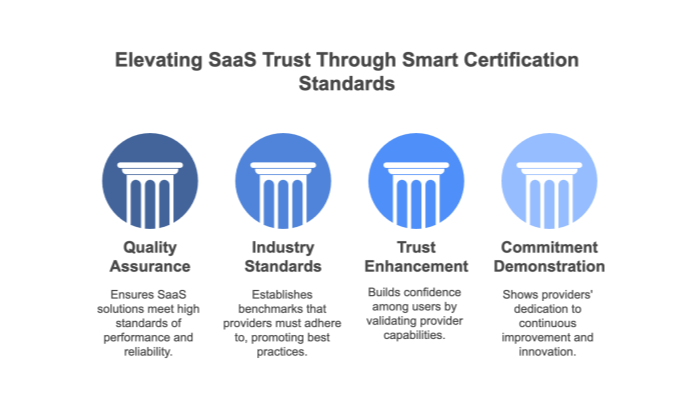
The concept of “Smart SaaS” certification is emerging as a means to ensure that vendors adhere to ethical, transparent data practices. In this section, we discuss how Smart SaaS principles can safeguard your data ownership. Certification ensures that vendors provide clear documentation on data handling, empower users with the ability to export their data without hidden fees, and guarantee robust security measures.
This framework emphasizes transparency, user agency, and data ownership, ensuring that you are not inadvertently locked into a vendor’s proprietary ecosystem. By choosing vendors that have achieved Smart SaaS certification, businesses can have greater confidence in the long‑term viability and ethical standards of their SaaS partners.

4. Contract Clauses for Data Ownership and Portability
A well‑structured contract is the foundation for securing your data rights. This section outlines essential clauses to negotiate with your SaaS vendor. Clear contract terms can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that you retain full control over your data.
By including explicit statements of ownership, detailed export mechanisms, defined data retention periods post‑termination, and robust security and encryption requirements, you can protect your organization from future risks. It is also vital to discuss costs and support related to data exports, ensuring that these services are provided without prohibitive fees. These contractual safeguards not only mitigate the risk of vendor lock‑in but also empower you to manage your data independently.
4.1 Explicit Data Ownership Statement
The most fundamental clause in any SaaS contract should be an unequivocal statement that the customer fully owns their data, ensuring the vendor cannot claim any rights beyond providing the agreed service. Without clear ownership terms, businesses risk losing control over how their data is used or accessed.
- Ownership Clarity: The contract must explicitly state that all data provided, processed, and stored within the SaaS platform remains the sole property of the customer, regardless of where it resides.
- Usage Restrictions: Vendors should not have the right to resell, analyze, or repurpose customer data beyond the agreed-upon service. Some providers insert vague clauses allowing broad data usage for internal analytics—this must be clearly restricted.
Without these protections, companies may find themselves in data-sharing arrangements they never agreed to, putting privacy, compliance, and competitive advantage at risk.
4.2 Detailed Export Mechanisms
Even if data ownership is established, businesses must ensure they can easily retrieve their information without excessive effort, costs, or limitations. Many SaaS vendors make exports cumbersome by restricting formats, excluding key metadata, or limiting export frequency.
- Frequency and Format: Contracts should specify how often full data exports are available and ensure they are provided in open-standard formats such as CSV, JSON, or XML, which are widely supported for integration and migration.
- Granularity: Data exports should include all relevant fields, including associated metadata, timestamps, logs, and audit trails. Without this, businesses may lose valuable insights or face data integrity issues when transitioning.
A robust export policy prevents businesses from being forced to stay with a vendor due to lack of migration readiness or incomplete datasets.
4.3 Data Retention Post-Termination
One of the biggest risks in data portability is the immediate deletion of customer data upon contract termination. Many SaaS vendors purge accounts quickly, leaving businesses with little to no time to retrieve mission-critical data.
- Retention Period: Contracts should mandate a reasonable grace period (e.g., 30 to 90 days) post-termination, during which businesses can securely export their data before deletion occurs.
- Deletion Policies: The contract must specify when and how data will be permanently deleted, ensuring it is erased from all primary and backup systems after the retention period expires.
Without clear retention and deletion terms, businesses may find themselves scrambling for last-minute backups or, worse, losing access to compliance-critical records.
4.4 Security and Encryption Requirements
A strong SaaS contract must also guarantee data security, ensuring information is protected at all times, even during transfers or exports. Many providers claim "secure storage," but without contractual commitments to encryption standards, businesses may be unknowingly exposing sensitive data.
- Encryption Standards: The contract should mandate that all customer data is encrypted both in transit and at rest using industry-standard protocols such as AES-256 encryption for storage and TLS 1.2+ for data transmission.
- Key Management: Vendors should detail encryption key management practices, ensuring keys are stored securely and that businesses retain access control options.
Without explicit encryption policies, businesses may fall short on compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2) or face security risks if the vendor suffers a breach.
4.5 Costs and Support for Exports
Even when SaaS vendors allow data exports, some introduce hidden costs that make it financially impractical for businesses to retrieve their own data. Unexpected charges for bulk exports, API access, or migration support can significantly inflate costs.
- No Excessive Fees: The contract should clearly state that full data exports are included in the service or available at a nominal, reasonable cost. Avoid vendors that charge steep fees per GB of exported data or restrict API-based extractions to expensive enterprise plans.
- Support Services: The vendor should provide reasonable assistance for data migration, ensuring customers can retrieve, verify, and reformat their data without requiring third-party intervention.
By addressing cost transparency upfront, businesses can avoid unexpected financial barriers that prevent them from leaving a SaaS provider when needed.

5. Best Practices for Data Control in a SaaS Environment
To ensure that your data remains secure and fully under your control, adopting best practices for data management in a SaaS environment is essential. In this section, we explore strategies such as conducting a comprehensive data inventory, scheduling regular backups, testing data restoration processes, monitoring vendor roadmap changes, and incorporating data portability into your vendor selection criteria.
By proactively managing these aspects, you can protect your organization from unforeseen data loss and maintain compliance with regulatory standards. These practices not only safeguard your data but also provide a safety net that enables smooth transitions between vendors, ensuring continuous operational resilience.
5.1 Conduct a Data Inventory
Understanding what data you store, where it resides, and how it’s used is critical for ensuring effective data management and portability. Without a clear inventory, businesses risk losing track of critical assets, facing compliance gaps, or struggling with incomplete exports when transitioning between platforms.
- Identify Critical Data: Perform a comprehensive audit of all data stored within the SaaS environment, including customer records, transaction logs, analytics, and compliance-related information.
- Prioritize Data: Classify data based on business-critical importance, regulatory requirements, and operational necessity. Focus on securing and regularly backing up high-priority datasets that would be costly or disruptive to lose.
A well-maintained data inventory ensures that organizations always know what they need to protect and migrate, minimizing the risk of data fragmentation or loss.
5.2 Set a Schedule for Regular Backups
Even if a SaaS vendor claims to manage redundancy and failover, businesses must maintain independent backups to prevent data loss, corruption, or unexpected vendor outages. Without a structured backup strategy, organizations risk losing access to critical data in the event of account termination, security breaches, or accidental deletions.
- Automated Exports: Set up scheduled data exports at regular intervals to ensure a local backup copy is always available. Vendors that do not support automated exports should raise concerns about data accessibility and lock-in risks.
- Backup Frequency: Choose an appropriate frequency based on business needs—weekly or monthly backups are standard, but mission-critical data may require daily snapshots to ensure continuity and recovery readiness.
Implementing a disciplined backup strategy ensures businesses remain in control of their data and prepared for any disruptions.
5.3 Test Data Restoration
A backup is only as good as its ability to be restored. Many companies assume their exported data is fully functional, only to discover issues when they actually need to use it. Without regular data restoration tests, organizations risk incomplete, corrupted, or unusable backups.
- Regular Testing: Perform periodic test restores in a sandbox environment to verify data integrity and usability.
- Verify Completeness: Ensure all key data fields, metadata, and dependencies are correctly restored, maintaining the original structure and relationships.
Regularly validating backup restoration processes ensures that, if a migration or recovery is ever needed, no time is wasted troubleshooting avoidable issues.
5.4 Watch for Shifts in the Vendor’s Roadmap
SaaS providers evolve their platforms continuously, sometimes introducing feature limitations, pricing changes, or API restrictions that may impact data accessibility. Businesses must proactively monitor vendor updates to avoid being blindsided by unexpected restrictions.
- Monitor Announcements: Stay informed about roadmap updates, new policies, and changes to pricing or service tiers that may affect data portability.
- Review Contract Amendments: Whenever the vendor modifies terms of service, reassess how it impacts data handling rights, export capabilities, and long-term accessibility.
By staying ahead of vendor shifts, organizations can anticipate risks early and make informed decisions about migration or contract renegotiation.
5.5 Incorporate Data Portability in Vendor Selection Criteria
Selecting the right SaaS provider from the start can prevent future lock-in issues. Many businesses focus solely on features and cost, overlooking how easy it will be to retrieve their data if they ever need to leave.
- Evaluate Portability: Choose vendors that offer transparent, standardized data export options and avoid those using proprietary formats or API limitations.
- Seek References: Request case studies or direct customer references showcasing successful migrations, proving the vendor supports true data portability.
Prioritizing data portability upfront ensures businesses retain control over their information, reducing long-term risks associated with restricted data access.

6. Avoiding SaaS Vendor Lock-In: Integration and Openness
Integration is a key strategy to mitigate the risk of vendor lock‑in. In this section, we discuss methods to ensure your SaaS environment remains flexible and interoperable. By leveraging standard APIs, iPaaS solutions, and even multi‑cloud or hybrid approaches, you can reduce dependence on a single vendor’s proprietary ecosystem.
These practices ensure that your data can be easily transferred, integrated, and analyzed across various platforms, thereby preserving your ability to switch vendors or adapt to new technologies as your business evolves.
6.1 Embrace Standard APIs
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) enable data flow between different software systems, but not all APIs are created equal. Many SaaS vendors lock users into their ecosystem by offering proprietary or poorly documented APIs, making integration complex and migration challenging.
- Use Open Standards: Choose SaaS platforms that support widely accepted API formats such as RESTful APIs using JSON or XML, ensuring smooth data exchange across multiple systems.
- Documentation: Well-documented APIs are crucial for integration success. Ensure that the vendor provides clear, updated API documentation with guidelines on authentication, rate limits, and error handling.
By standardizing API usage, businesses reduce integration complexity and gain more flexibility to switch vendors when needed.
6.2 Use iPaaS Solutions
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solutions help organizations connect multiple SaaS applications without relying on custom, vendor-specific integrations. iPaaS acts as a middleware layer, enabling data flow automation and workflow orchestration across different platforms.
- Centralize Integrations: iPaaS solutions like MuleSoft, Zapier, or Workato allow businesses to manage multiple SaaS connections in a single interface, reducing integration maintenance burdens.
- Flexibility: Unlike direct SaaS-to-SaaS connections, iPaaS allows businesses to reroute data flows or replace applications without disrupting entire workflows, making vendor changes less risky and more manageable.
By using iPaaS, companies future-proof their integrations, ensuring scalability and adaptability as business needs evolve.
6.3 Leverage Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Approaches
Relying solely on a single SaaS provider increases business risk and dependency. A multi-cloud or hybrid strategy allows companies to retain control over critical data while benefiting from cloud scalability.
- Reduce Dependency: Keeping some data and workloads in private or hybrid cloud environments prevents complete reliance on a single vendor, ensuring business continuity in case of disruptions or price hikes.
- Secure Flexibility: A vendor-agnostic architecture enables businesses to quickly shift workloads and migrate data between providers without experiencing downtime or compliance issues.
Adopting multi-cloud and hybrid models ensures long-term flexibility, allowing businesses to stay agile and responsive to both market changes and SaaS limitations.

7. Real-World Examples: Data Ownership Pitfalls and Successes
Examining real-world scenarios can illuminate the practical implications of data ownership in a SaaS environment.
This section highlights both pitfalls and successes to provide a balanced view. By learning from the experiences of other organizations, you can better prepare for potential challenges and implement strategies that safeguard your data. These examples underscore the importance of negotiating clear contracts and maintaining regular backups to avoid costly disruptions or forced vendor upgrades.
7.1 Pitfall: SMB Marketing Agency Held Hostage by CRM SaaS
Scenario:
A small marketing agency adopted a CRM SaaS solution that initially fit its budget and workflow. Over time, the agency realized that critical client data—including detailed client notes and historical interactions—was locked behind a premium-tier paywall.
When the agency needed full access to its own data, the SaaS vendor forced an expensive upgrade, significantly increasing operational costs. Without clear data export policies in place, the company faced a difficult choice:
- Pay the inflated fees to access its own historical records
- Attempt a time-consuming, manual data extraction
- Lose valuable client data and start fresh with a new platform
Key Takeaways:
- Always review SaaS pricing structures for data access restrictions before committing.
- Negotiate upfront data ownership clauses that prevent paywalls from blocking critical exports.
- Test export functionality early to confirm all data (including notes, logs, and metadata) is retrievable.
7.2 Success Story: Healthcare Provider Minimizes Lock-In
Scenario:
A mid-sized healthcare group implemented a HIPAA-compliant SaaS platform for managing patient records and scheduling. Aware of the risks of vendor lock-in, the company negotiated strong data ownership clauses in the contract and implemented a proactive data export strategy:
- Automated CSV exports of all patient records, ensuring local backups were always available.
- Defined retention and deletion policies to maintain control over patient history.
- Ensured compliance with HIPAA and industry standards by mandating data portability.
When the SaaS vendor later introduced a disruptive pricing model and feature overhaul, the healthcare provider was able to migrate seamlessly to a new system without:
- Losing patient data
- Paying excessive migration fees
- Experiencing major service downtime
Key Takeaways:
- Negotiate strong data ownership clauses to guarantee full access and portability.
- Implement automated, scheduled exports to maintain control over critical records.
- Have a contingency plan for switching vendors without data loss.

8. Combining Data Ownership with Security and Compliance
In regulated industries, data ownership and portability must work hand in hand with robust security and compliance practices. This section discusses how to ensure that your data remains both accessible and secure. By implementing rigorous data classification, enforcing security standards as a baseline, and performing ongoing risk assessments, organizations can create a resilient data strategy. These measures not only help protect sensitive information but also ensure that your data remains compliant with industry regulations, thereby reducing legal risks and enhancing business agility.
8.1 Data Classification and Compliance
Every organization handling sensitive or regulated data must ensure that export and storage practices align with legal and industry requirements. SaaS providers may claim compliance, but the ultimate responsibility for regulatory adherence falls on the customer.
- Regulatory Alignment: Before exporting data, ensure it complies with standards such as HIPAA (healthcare), GDPR (EU data privacy), PCI DSS (financial transactions), or SOC 2 (data security best practices). Non-compliance can result in fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
- Encryption: All data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest during exports and transfers. AES-256 encryption for storage and TLS 1.2+ for data transmission should be mandatory to prevent interception and unauthorized access.
By implementing strict compliance protocols, businesses protect their customers, avoid penalties, and maintain regulatory readiness.
8.2 Security as a Standard, Not a Luxury
Many SaaS vendors limit security features to premium pricing tiers, forcing businesses to pay extra for essential protections. However, security should be a baseline expectation, not an upsell opportunity.
- Built-In Protections: Critical security features such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access controls (RBAC), audit logs, and real-time threat monitoring should be included in all service tiers—not hidden behind expensive upgrades.
- Continuous Monitoring: Organizations must implement regular security assessments to detect vulnerabilities, monitor for unauthorized access, and verify that SaaS vendors uphold security commitments.
By demanding strong security standards from the start, businesses can prevent costly breaches and reduce long-term risks.
8.3 Ongoing Risk Assessments
Security threats evolve continuously, making one-time compliance checks inadequate. A proactive risk assessment framework ensures data security policies remain effective and adaptable as business environments change.
- Regular Reviews: Businesses should routinely evaluate security measures, especially when adding new integrations, expanding user access, or switching vendors.
- Adaptability: Risk management policies should be updated frequently to address new cybersecurity threats, evolving regulatory requirements, and changes in business operations.
A continuous risk assessment approach ensures long-term data security and compliance, reducing the likelihood of unexpected vulnerabilities or regulatory failures.

9. Take Control of Your SaaS Data—Don’t Be a Hostage
In the era of SaaS dominance, controlling your data is paramount. Without robust data ownership and portability, organizations risk becoming hostage to their vendors—facing unexpected price hikes, forced upgrades, or even complete data loss. The key is to ensure that your contracts, technology, and processes empower you to export and manage your data independently.
By following the principles of transparency, agency, and security as outlined in the eBook Escape the SaaS Trap, you can negotiate favorable terms and implement best practices that protect your most valuable asset. When your data is truly under your control, you gain the freedom to adapt, innovate, and thrive without being shackled by vendor constraints. Ultimately, safeguarding data ownership is not just a technical issue—it is a strategic imperative for sustainable business success.
Key Takeaways:
- Prioritize Data Ownership: Ensure all contracts clearly state that your data remains yours.
- Regular Backups: Schedule frequent data exports and test restoration processes.
- Negotiate Favorable Terms: Include clauses for export mechanisms, retention periods, and minimal fees.
- Embrace Open Integrations: Use standard APIs and iPaaS solutions to prevent vendor lock‑in.
- Align with Smart SaaS: Choose vendors who commit to transparency, security, and user empowerment.

10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below are answers to common questions regarding SaaS data ownership and portability, helping you ensure that your organization retains full control over its data.
-
What is SaaS data ownership?
It means that you, the customer, retain exclusive rights to all data stored within a SaaS platform. The vendor hosts it but does not control its usage or export.
-
Why does data portability in SaaS matter?
Data portability enables you to switch vendors, integrate with other systems, and comply with regulatory requirements by ensuring that you can export your data in open-standard formats.
-
What contract clauses protect my data?
Look for explicit ownership statements, detailed export mechanisms, defined data retention periods after termination, and clear security and encryption requirements.
-
How often should I back up my SaaS data?
Ideally, perform weekly or monthly exports and store them securely. Regular testing of these backups is also essential.
-
Can a vendor delete my data if I end the subscription?
Typically, yes—after a specified grace period. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that allow a final export before data deletion.
-
How does “Smart SaaS” address data ownership?
“Smart SaaS” vendors provide transparent data policies, easy export procedures, and ethical contract terms that guarantee your control over your data.