

Sunday, February 2, 2025
Kevin Anderson
Building a successful SaaS business model requires more than just offering software on a subscription basis. It demands a thorough understanding of market needs, a scalable product strategy, and the ability to balance customer acquisition with retention. The SaaS model has gained immense popularity due to its predictable revenue streams, cost‑efficiency, and scalability, making it one of the most lucrative frameworks for modern businesses.
This guide will walk you through the key components, actionable steps, and proven strategies for creating a SaaS business that not only meets market demands but also thrives in a competitive landscape. Whether you’re a startup founder or an established entrepreneur, this roadmap will help you craft a business model designed for sustainable growth.

The SaaS business model is based on delivering software through the cloud on a subscription basis. Unlike traditional software, which is purchased outright and installed locally, SaaS platforms allow users to access applications via the internet, with providers managing maintenance, updates, and security.

By leveraging cloud computing and offering subscription‑based access, SaaS empowers businesses to minimize upfront costs and streamline operations.
| Feature | SaaS Model | Traditional Software |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery | Cloud‑based, accessed online | Installed on individual devices |
| Pricing | Subscription‑based, pay‑as‑you‑go | One‑time license fee |
| Maintenance | Managed by the provider | Managed by the user |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited to existing hardware |
| Access | Anywhere with internet | Restricted to specific devices |
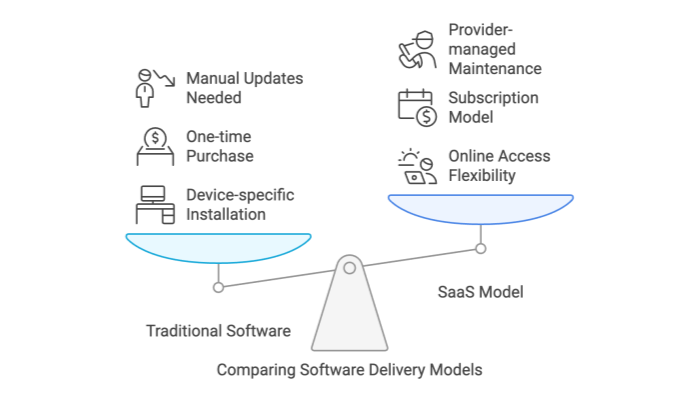

The SaaS business model stands out as one of the most effective and scalable frameworks for modern businesses. By combining predictable revenue streams with customer‑centric delivery, SaaS has transformed how companies offer and consume software. Here’s why SaaS is widely regarded as the best business model in the digital era:
SaaS thrives on its subscription‑based pricing, which ensures a steady and predictable flow of revenue. Unlike traditional software sales that rely on one‑time purchases, SaaS generates Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), providing financial stability. For example, a SaaS company with 1,000 customers paying $50 per month generates $50,000 in predictable MRR. This predictable cash flow simplifies financial planning and makes it easier to forecast growth, allocate resources, and secure funding.
SaaS solutions are inherently scalable, catering to the needs of small startups and large enterprises alike. Customers can adjust their subscription plans based on usage, team size, or budget, making SaaS highly flexible. For startups, affordable entry‑level plans help businesses access essential tools without significant upfront costs. For enterprises, advanced tiers offer robust functionality, integrations, and support to meet complex needs.
Traditional software often required expensive licenses and dedicated infrastructure, creating barriers for small businesses. SaaS eliminates these hurdles by offering freemium models and pay‑as‑you‑go plans. Customers pay only for the resources they use, making SaaS cost‑effective and accessible.
The success of a SaaS business is closely tied to its ability to meet customer needs consistently. SaaS platforms prioritize user experience (UX) and customer success, ensuring users derive ongoing value from the software. Features like intuitive interfaces, continuous updates, and proactive customer support drive success.
The SaaS model is not only scalable for customers but also for providers. Cloud infrastructure enables SaaS companies to accommodate thousands of users without significant hardware investments and to scale resources dynamically. For example, companies like Zoom scaled effortlessly during the pandemic, supporting millions of new users without service disruption.
SaaS emphasizes building long‑term relationships with customers, which results in high retention rates and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). Retaining a customer often costs less than acquiring a new one, making retention strategies critical to SaaS profitability.
SaaS platforms operate on the cloud, allowing companies to expand their reach without physical infrastructure. Providers can target global markets by supporting multiple languages, currencies, and region‑specific compliance features.
SaaS companies thrive on innovation, as the model incentivizes frequent updates and new features. Unlike traditional software that stagnates after purchase, SaaS evolves constantly to meet changing market needs.
The predictable revenue and scalability of SaaS businesses make them highly attractive to investors. Key metrics like Net Revenue Retention (NRR) and Annual Contract Value (ACV) demonstrate growth potential and help secure funding for expansion.
The SaaS model is built for resilience, with recurring revenue and scalable operations providing a buffer against economic downturns. By focusing on customer retention and recurring income, SaaS businesses can weather market fluctuations effectively.

Building a thriving SaaS business model requires strategic planning, customer focus, and operational efficiency. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring scalability, profitability, and long‑term sustainability.
The backbone of the SaaS model is its predictable, recurring revenue. This includes subscription‑based pricing and freemium models that allow for steady cash flow.
A successful business model focuses on creating value for users and ensuring a seamless experience through intuitive onboarding and proactive support.
Utilizing cloud platforms to design systems that can handle increased demand is crucial. This ensures that as your customer base grows, your platform remains robust.
Choosing a pricing strategy that aligns with customer value and market demand is essential. Options include tiered pricing, usage‑based pricing, and freemium models.
Retention strategies such as personalized onboarding, continuous updates, and customer success teams help reduce churn and boost customer lifetime value.
Monitoring key metrics like MRR, CAC, and churn rate allows SaaS businesses to make informed decisions and optimize growth.
Robust APIs and integration capabilities ensure that the SaaS product can connect with existing systems and workflows.
Ensuring data protection through encryption, multi‑factor authentication, and regulatory compliance is paramount.
Continuous product improvement through agile methodologies keeps the platform competitive and aligned with customer needs.
A unified strategy between marketing and sales is critical to acquiring and retaining customers effectively.

Success in SaaS relies on tracking and optimizing specific KPIs. These metrics provide insights into growth, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
MRR is the predictable income generated from subscriptions each month. It’s calculated as Total Active Customers × Average Revenue Per User (ARPU). For example, 500 customers paying $50/month equals $25,000 in MRR.
ARR expands on MRR by projecting yearly revenue. It is calculated as MRR × 12.
Churn Rate measures the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions. It is calculated as (Customers Lost ÷ Total Customers at Start) × 100.
CLV represents the total revenue a customer generates over their lifetime. It is calculated as ARPU × Average Customer Lifetime (in months). This metric informs decisions about customer acquisition spending.
CAC is the cost of acquiring a new customer, calculated as Total Sales and Marketing Expenses ÷ New Customers Acquired.
NRR measures the revenue retained from existing customers, factoring in upgrades, downgrades, and churn. It is calculated as (Starting Revenue + Expansion Revenue - Churn Revenue) ÷ Starting Revenue × 100.
Gross Margins measure the profitability of a SaaS business after accounting for the costs of delivering the service, calculated as (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) ÷ Revenue × 100.
MAU tracks the number of unique users engaging with the product each month.
This metric measures the percentage of trial users who convert to paying customers, indicating the effectiveness of the onboarding process.
Expansion Revenue is the additional income generated from existing customers through upselling, cross‑selling, or renewals—a key driver of growth.
Tracking these metrics enables SaaS businesses to make data‑driven decisions, improve customer retention, and optimize profitability.

While the SaaS business model offers significant advantages like recurring revenue and scalability, it also presents unique challenges that businesses must address for sustainable growth.
High churn rates directly impact revenue and growth. Common causes include poor onboarding, misalignment between product features and customer needs, and inadequate customer support. Solutions involve improving onboarding, engaging customers proactively, and using predictive analytics to identify at‑risk users.
High CAC, driven by expensive marketing campaigns and inefficient lead generation, can strain profitability. Targeted marketing, freemium models, and optimized sales funnels can help reduce the CAC payback period.
Retaining existing customers is critical, as it is often more cost‑effective than acquiring new ones. Continuous product updates, proactive support, and loyalty programs are essential to reduce churn.
Operating in a multi‑tenant cloud environment increases risks related to data breaches and regulatory compliance. Robust encryption, multi‑factor authentication, and regular security audits are vital to mitigate these risks.
As the customer base grows, operational costs such as cloud infrastructure, support, and maintenance can rise. Efficient cloud management and automation can help control these costs.
The SaaS market is highly competitive. Differentiating your product through innovation, strong branding, and exceptional customer service is crucial.
Dependence on a single vendor can restrict flexibility and make switching providers difficult. Open APIs, transparent contracts, and data portability are key to avoiding vendor lock‑in.
Customer expectations evolve rapidly, so SaaS providers must continuously innovate and update their offerings. Regular feedback and agile development practices help maintain relevance.
Addressing these challenges is essential for building a resilient SaaS business. By focusing on customer retention, optimizing costs, and staying ahead of security risks, providers can overcome obstacles and deliver consistent value.

Salesforce revolutionized CRM by introducing cloud‑based solutions that transformed how businesses manage customer relationships. Key features include subscription‑based revenue, enterprise focus, and an expansive app marketplace. Its scalability and continuous innovation have made it a leader in the SaaS space.
Slack provides a seamless messaging platform that integrates with numerous tools, offering a user‑friendly interface for team communication. Its freemium model and extensive integrations have driven widespread adoption, creating a strong network effect.
Zoom scaled rapidly during the pandemic, showcasing the power of cloud‑based video conferencing. Its freemium model and reliable performance made it indispensable for remote communication.
HubSpot offers comprehensive tools for marketing, sales, and customer service, with a strong focus on inbound marketing. Its freemium and tiered pricing models attract a diverse range of customers, and its customer‑centric approach drives high engagement.
Shopify empowers businesses to launch and manage online stores through its scalable e‑commerce platform. With various pricing tiers and a robust app marketplace, it serves a wide range of merchants, from startups to large enterprises.
Although known primarily as an entertainment platform, Netflix operates on a SaaS model for delivering streaming content. Its subscription‑based pricing and personalized content recommendations have transformed how consumers access entertainment.
Adobe transformed its traditional software licenses into a SaaS model with Creative Cloud, offering tools like Photoshop and Illustrator on a subscription basis. Its continuous updates and strong brand loyalty have made it indispensable for creative professionals.


Creating a successful SaaS business model requires a combination of strategic planning, market research, and a deep understanding of customer needs. Below is a step‑by‑step guide:
Before investing time and resources, ensure there is a demand for your SaaS product.
Pricing is a critical component that affects customer acquisition, retention, and revenue. Common models include tiered pricing, freemium, usage‑based pricing, and flat‑rate pricing.
Example: Slack uses a freemium model, offering free basic plans with paid options for advanced features like increased storage.
Your product must grow with your customer base while maintaining performance and usability.
Attracting customers is a key challenge. A well‑rounded acquisition strategy ensures a steady flow of new users.
Retaining existing customers is often more cost‑effective than acquiring new ones. Prioritize customer retention to boost long‑term profitability.
Data‑driven decisions are essential for growth. Monitor key metrics such as Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), churn rate, and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) to refine your strategy.
Once your SaaS model is established, scaling operations to accommodate new markets and customers is crucial.

Building a successful SaaS business model is a journey that combines innovation, customer focus, and strategic execution. By validating your idea, designing scalable solutions, and prioritizing customer retention, you can create a SaaS business that thrives in a competitive landscape.
For more detailed insights on building and scaling your SaaS business, download our eBook: Don’t Get SaaS’d – A B2B Buyer’s Guide and unlock actionable strategies to achieve success in the SaaS industry.