
Tuesday, February 18, 2025
Kevin Anderson
Software as a Service (SaaS) fundamentally changed how businesses access and pay for software. Instead of hefty upfront licenses, companies now pay a monthly or annual fee for ongoing access to cloud‑based tools. However, this financial convenience can lead to confusion when billing structures are not fully transparent. Hidden overage charges, tier‑based “gotchas,” and opaque billing schemes may result in unexpected cost overruns and even vendor lock‑in scenarios.
In this post, we dissect SaaS billing platforms—the systems that automate recurring charges, handle usage‑based fees, and manage payment workflows. We will also explain how to track your SaaS spend effectively, highlight the differences between transparent and opaque billing, and tie in the principles of “Smart SaaS” from the eBook Escape the SaaS Trap. By understanding how automated billing works under the hood, you can defend against hidden charges, demand flexibility, and ensure you’re not paying for unnecessary features.
Use the links below to navigate through the article:

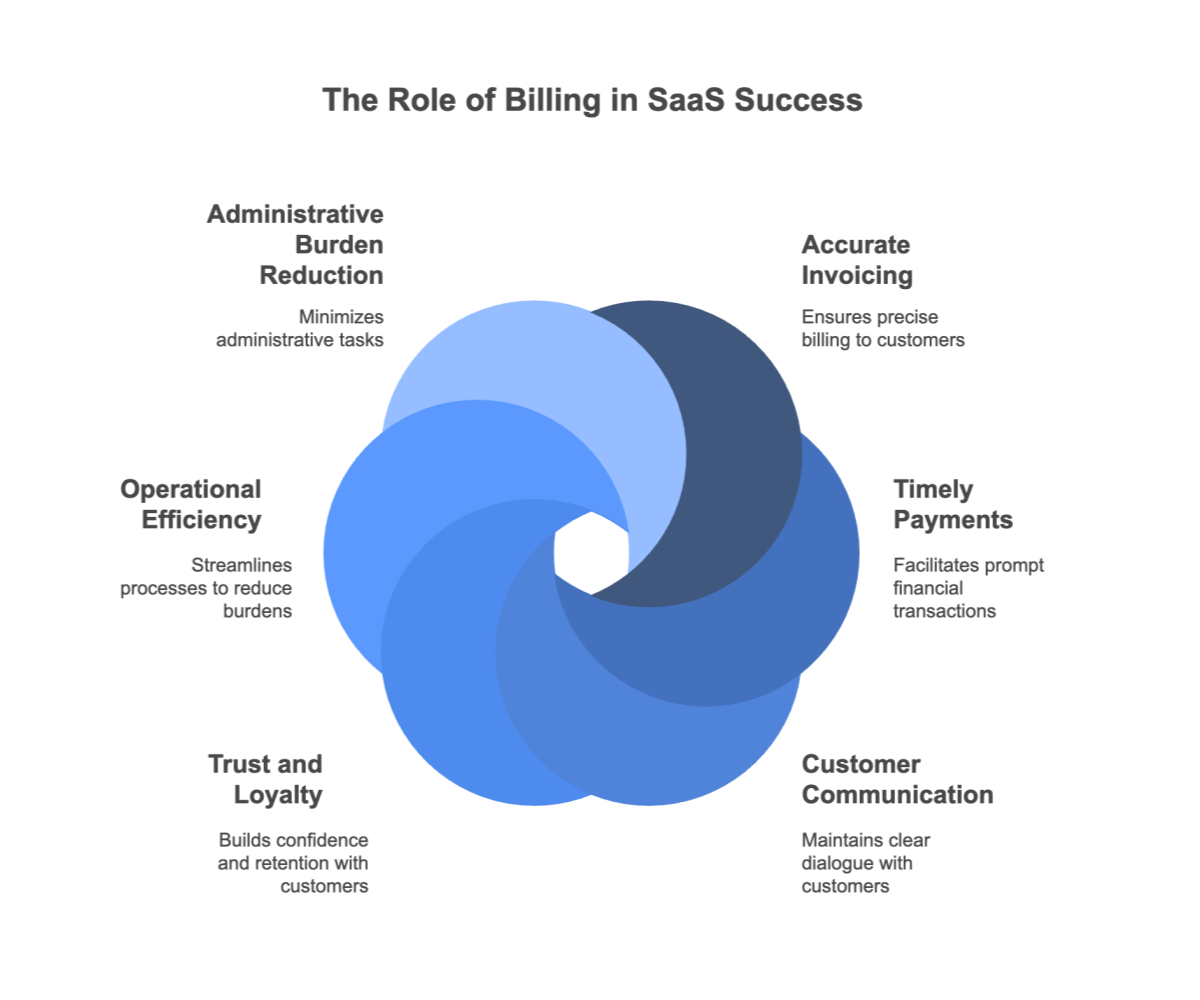
Billing is the financial heartbeat of any SaaS business. The shift from traditional software licensing to a subscription‑based model has provided companies with flexibility and predictable cash flows. However, this change also introduces new challenges in managing recurring costs and usage‑based fees. In this section, we explore the evolution of subscription‑based software, discuss its benefits, and outline the hidden risks that may emerge if billing is not managed transparently.
A clear understanding of billing structures is critical not only for budgeting but also for negotiating fair terms and avoiding vendor lock‑in. By examining both the advantages and pitfalls of subscription-based billing, organizations can better plan for growth, manage their expenses, and ensure that they are not overpaying for their SaaS tools. The following subsections break down these concepts into detailed points, helping you grasp why a meticulous approach to SaaS billing is indispensable.
Key Points:
- Lower Barriers to Entry: Companies pay smaller recurring fees rather than huge upfront costs.
- Continuous Updates: Customers always have access to the latest features without manual upgrades.
- Easier Budgeting: Operating expenses replace capital expenditures, smoothing out cash flow.
Additional Context: As noted in the eBook Escape the SaaS Trap, these benefits come with risks such as hidden price increases and forced upgrades, which may catch subscribers off guard.
Key Points:
- Simplified Invoicing: Automated systems handle recurring payments, reducing manual work.
- Potential for Hidden Costs: Lack of transparency can lead to unanticipated charges and overage fees.
- Risk of Vendor Lock-In: Automated billing may obscure true usage metrics, making it harder to switch vendors.
Additional Context: Although automated billing offers convenience by eliminating manual invoicing, it can also hide details such as exact seat counts and usage data. This may result in surprises on your invoice and difficulty in managing your budget.

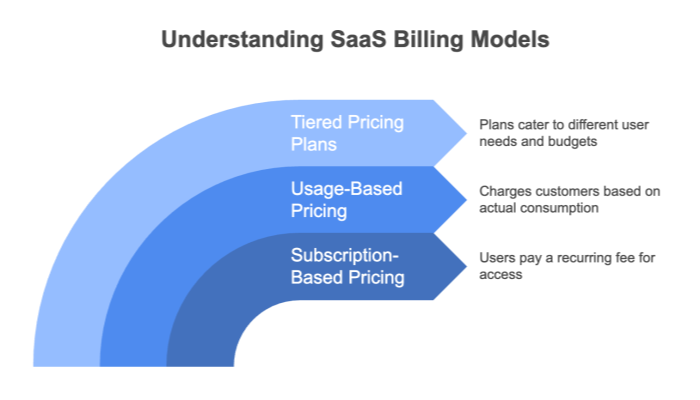
There are several billing models employed by SaaS vendors, each with its own benefits and potential drawbacks. Understanding these models is essential for selecting a solution that aligns with your business needs and usage patterns. In this section, we detail the primary billing models—seat‑based, usage‑based, tier‑based/bundled plans, and hybrid models—explaining their mechanics and the pros and cons associated with each approach.
Overview:
- Simple and Predictable: Charges per user seat make it easy to forecast expenses.
- Scalability Issues: Rapid team growth may double costs, encouraging license hoarding or under-provisioning.
Additional Context: This model is common in collaboration and CRM tools, where the cost directly scales with the number of users. However, it can discourage optimal usage if companies limit seats to avoid rising costs.
Overview:
- Cost-Efficient: Pay only for what you use, ideal for fluctuating workloads.
- Risk of Overage Fees: Sudden surges in usage can trigger expensive overage charges.
Additional Context: Usage-based models are prevalent in data-heavy applications and cloud infrastructure services. The key is to monitor usage metrics closely to prevent unexpected billing spikes.
Overview:
- Simplified Choice: Pre-defined tiers make it easy to choose a plan based on features and support levels.
- Opaque Upgrades: Essential features may be locked behind higher tiers, forcing an upgrade even if only one extra feature is needed.
Additional Context: Tier-based pricing is effective for standardizing offerings, but be cautious of bundled features that you may not require, leading to unnecessary costs.
Overview:
- Flexible: Combines seat‑based and usage‑based elements, offering tailored billing solutions.
- Complexity: May lead to confusion if the vendor’s pricing details are not fully transparent.
Additional Context: Hybrid models aim to capture the benefits of multiple billing approaches but require careful analysis to avoid unexpected fees and ensure that the pricing structure aligns with your actual usage.

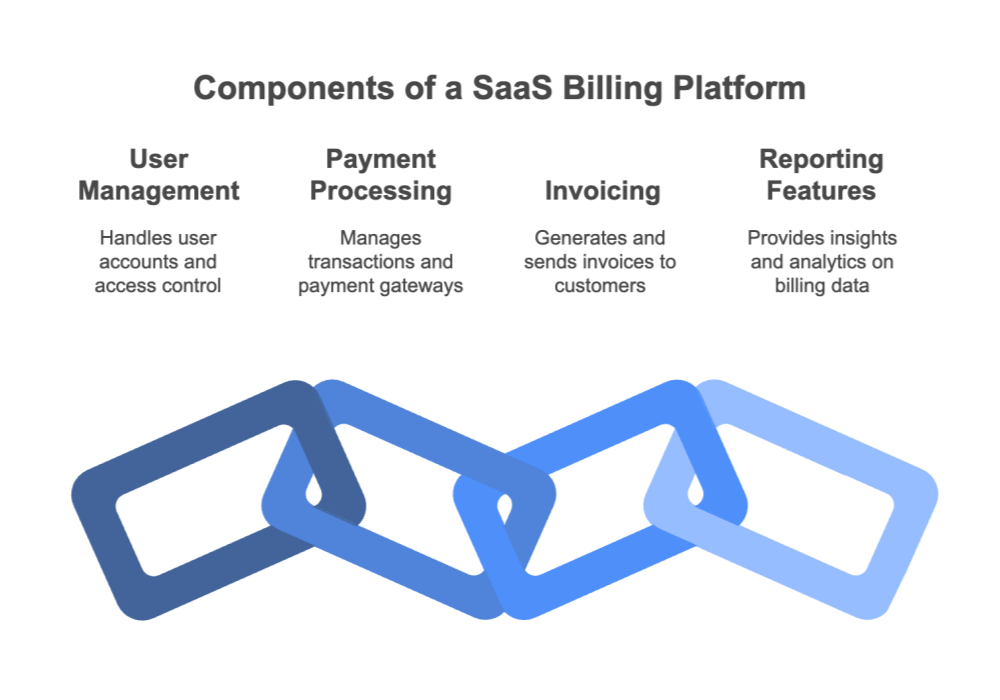
A SaaS billing platform is the engine that automates recurring payments and manages complex billing structures. It integrates various components such as subscription management, payment processing, invoicing, tax handling, dunning management, and reporting. In this section, we break down the anatomy of these platforms, emphasizing how each component contributes to a seamless billing experience. By understanding the inner workings of billing platforms, organizations can better track costs, predict future expenses, and ensure a smooth revenue cycle.
Core Functions Include:

Understanding the differences between transparent and opaque billing practices is critical for managing SaaS expenses effectively. Transparent billing provides clear, detailed invoices and real‑time usage dashboards, allowing you to predict and control costs. In contrast, opaque billing practices hide key details, leading to surprise charges and reduced control over your spending. In this section, we compare both approaches and explain how to identify which practices to embrace and which to avoid.
Key Attributes:
- Itemized Invoices: Detailed breakdown of costs by seat, usage tier, and add-ons.
- Real-Time Dashboards: Up‑to‑date metrics on usage and upcoming charges.
- Predictable Overage Fees: Clear communication when thresholds are reached.
- Flexible Upgrade Paths: No forced multi‑year contracts for temporary needs.
Red Flags:
- Surprise Charges: Hidden fees that only appear after usage spikes.
- Complex Tier Definitions: Unclear metrics that make it difficult to determine the best plan.
- Retroactive Billing: Fees added at the end of the billing period without prior notice.
- Lack of Detailed Invoices: Lump‑sum charges that prevent cost allocation and verification.

Despite the promise of predictable subscription costs, hidden fees can catch SaaS users off guard. Vendors may include additional charges that are not immediately apparent, which can significantly impact your overall expenditure. This section delves into the common types of hidden fees, including add‑on service charges, payment gateway fees, ambiguous maintenance fees, and forced upgrades. Understanding these hidden costs is crucial to ensure that you are not paying more than expected and that your SaaS investment remains cost‑effective.
Examples:
- Premium Support: Extra charges for expedited or in‑depth customer support.
- Security Features: Advanced security options like SSO or encryption may come at an extra cost.
- Custom Domains/Branding: White‑labeling the software often requires a higher‑priced plan.
Key Considerations:
- Some platforms add a percentage fee on every transaction.
- These fees can erode profit margins, especially for high‑volume e‑commerce businesses.
Issues:
- Vendors may add ambiguous fees for ongoing platform improvements or maintenance, which are not clearly disclosed in the contract.
Warning:
- Automatic transitions to higher‑tier plans without adequate notice can force an unwanted increase in subscription fees.

Effective management of SaaS spending is essential to avoid unexpected cost escalations. This section outlines strategies to track, audit, and control your SaaS expenditures. With a structured approach, you can identify unused licenses, monitor usage-based fees, and ensure that your subscription costs remain aligned with your business needs. By implementing rigorous tracking methods and leveraging centralized dashboards, you can maintain transparency and proactively manage your SaaS spend, ultimately saving money and optimizing operational efficiency.
Steps:
- Inventory Tools: List every SaaS application in use, including trials turned paid.
- Review Plan Tiers: Identify whether you are on a basic, professional, or enterprise plan.
- Check Renewal Dates: Note when each subscription renews to avoid surprises.
Benefits:
- Consolidates all usage and cost data in one accessible location.
- Helps to avoid duplicate subscriptions and unplanned upgrades.
Key Features:
- Set internal triggers to warn when usage approaches plan limits.
- Enable notifications through email or messaging apps like Slack.
Action Steps:
- Regularly review active vs. inactive user accounts.
- Reassign or cancel unused licenses to immediately reduce costs.

Real-world examples often reveal how hidden billing practices can negatively impact an organization. This section presents case studies that illustrate the pitfalls of poorly managed SaaS billing. By examining these scenarios, you can learn valuable lessons to help avoid similar issues in your own SaaS environment. The examples highlight overpayments due to unnecessary enterprise features, unexpected transaction fees in e‑commerce, and the cumulative effect of multiple unmanaged subscriptions.
Scenario:
A mid‑sized digital marketing agency invested in a marketing automation tool. Initially, the basic plan was sufficient, but soon they found that key analytics and A/B testing features were locked behind an enterprise tier, causing their costs to quadruple. This forced upgrade significantly increased their monthly spend.
Scenario:
An e‑commerce startup subscribed to a platform that advertised a flat monthly rate with “no hidden charges.” Soon, a 2.5% transaction fee was applied to every sale, drastically reducing profit margins. The startup was unaware of these additional fees until they impacted the bottom line.
Scenario:
A tech company used a multitude of SaaS tools across different departments without centralized oversight. As each department added new subscriptions, total costs ballooned, and unexpected overage fees began to appear. By the end of the quarter, the overall SaaS spend had nearly doubled, with no corresponding increase in productivity.

To navigate the complexities of SaaS billing, companies must adopt strategies that ensure transparency, control, and adaptability.
This section provides actionable steps to maintain clarity in your billing processes. By adopting “Smart SaaS” principles, negotiating favorable contracts, and piloting new solutions before full implementation, organizations can avoid pitfalls such as hidden fees and vendor lock‑in.
These strategies will empower you to take charge of your SaaS spend and maintain a flexible, cost‑efficient subscription model that grows with your business.
Key Principles:
- Transparency: Vendors must provide clear itemized invoices and usage dashboards.
- Agency: Ensure you have the ability to add or remove seats without restrictive contracts.
- Data Ownership: Secure rights to export usage data and logs easily.
- Security: Confirm that robust security measures are in place.
Key Steps:
- Price Caps: Include clauses limiting mid‐contract price increases.
- Cancellation Windows: Secure the right to exit with minimal penalties.
- Data Portability: Ensure you can export all billing and usage data.
Guidelines:
- Look for detailed pricing documentation and usage calculators.
- Avoid “contact sales for pricing” models that lack transparency.
- Ensure vendors provide sample invoices for your anticipated usage.
Best Practices:
- Conduct a short, fully featured trial with a subset of your apps.
- Monitor seat allocation, transactions, and data usage closely.
- Verify that the vendor’s billing claims align with your actual experience.

SaaS billing platforms are designed to simplify subscription management by automating recurring payments, tracking usage-based costs, and consolidating billing data. When implemented correctly, these platforms can help organizations maintain control over their software spend and avoid unexpected fees. However, without transparent practices and clear contractual terms, an SMP can become just another costly layer of complexity. In conclusion, understanding your billing model—whether it’s seat‑based, usage‑based, tiered, or hybrid—is critical to avoiding surprises.
By adopting “Smart SaaS” principles, keeping a close eye on your spending, and negotiating favorable terms, you can transform subscription chaos into a well‑managed financial strategy that supports growth and innovation.
Key Takeaways:
- Know Your Billing Model: Understand the nuances of seat‑based, usage‑based, and tiered pricing.
- Monitor SaaS Spend: Use centralized tools to track and control costs.
- Demand Transparency: Insist on detailed invoices and real‑time dashboards.
- Negotiate Wisely: Secure favorable contract terms and exit clauses.
- Embrace “Smart SaaS”: Prioritize solutions that ensure data ownership, security, and flexibility.
Below are answers to common questions about SaaS billing platforms to help you better understand how these systems work and what to look out for.